| Date | Notes |
|---|---|
| 2020-06-02 | 首次提交 |
| 2020-06-16 | 增加「逻辑表达式」一节 |
Preface
Boolean,即布尔值,通常用来表明逻辑中的真或假。但在 Obj-C 中,我们似乎既可以使用 BOOL 又可以使用 bool,既可以使用 YES/NO 又可以使用 true/false,那么它们到底有何不同呢?
⚠️ 注意:
为了避免读者(和笔者)记混,这里简单说明下
#define与typedef的异同:#define A B意为将已存在的B定义为A,A与B等价;typedef C D意为将已存在的C定义为D,C与D等价;后者通常用于类型定义。
_Bool 与 bool
// iOS - stdbool.h
/*===---- stdbool.h - Standard header for booleans -------------------------===
*
* Part of the LLVM Project, under the Apache License v2.0 with LLVM Exceptions.
* See https://llvm.org/LICENSE.txt for license information.
* SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0 WITH LLVM-exception
*
*===-----------------------------------------------------------------------===
*/
#ifndef __STDBOOL_H
#define __STDBOOL_H
/* Don't define bool, true, and false in C++, except as a GNU extension. */
#ifndef __cplusplus
#define bool _Bool
#define true 1
#define false 0
#elif defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__STRICT_ANSI__)
/* Define _Bool as a GNU extension. */
#define _Bool bool
#if __cplusplus < 201103L
/* For C++98, define bool, false, true as a GNU extension. */
#define bool bool
#define false false
#define true true
#endif
#endif
#define __bool_true_false_are_defined 1
#endif /* __STDBOOL_H */
// ---
// macOS 10.15 - Frameworks - Kernel - stdbool.h
#ifndef _STDBOOL_H_
#define _STDBOOL_H_
#define __bool_true_false_are_defined 1
#ifndef __cplusplus
#define false 0
#define true 1
#define bool _Bool
#if __STDC_VERSION__ < 199901L && __GNUC__ < 3
typedef int _Bool;
#endif
#endif /* !__cplusplus */
#endif /* !_STDBOOL_H_ */
C 语言在 C99 标准诞生之前并没有原生的布尔类型,而 C99 标准为 C 语言提供了布尔类型,即 _Bool 关键字,但需要额外引入 stdbool.h 来使用。_Bool 的真值为 1 假值为 0。
The type
_Booland the unsigned integer types that correspond to the standard signed integer types are the standard unsigned integer types. The unsigned integer types that correspond to the extended signed integer types are the extended unsigned integer types. The standard and extended unsigned integer types are collectively called unsigned integer types.
_Bool类型与对应标准有符号整型的无符号整型类型是标准无符号整型类型。对应扩展有符号整型的无符号整型类型是扩展无符号整型类型。标准与扩展无符号整型类型统称为无符号整型。—— C99 §6.2.5.6
关于 _Bool 的底层类型,C99 标准中没有直接明确说明,但根据 C99 §6.2.5.6 我们可以认为 _Bool 属于 unsigned int,但实际仍只占用一个字节:
printf("%lu\n", sizeof(_Bool));
printf("%lu\n", sizeof(unsigned int));
// 1
// 4
在 stdbool.h 中,非 __cplusplus 情况(即未使用 C++ 编译器)下,_Bool 被宏定义为 bool,1 被宏定义为 true,0 被宏定义为 false。因此在引入 stdbool.h 的项目中,bool 就等同于 _Bool。不同于 C 语言,C++ 诞生即拥有原生的布尔类型 bool,其真值为 true 假值为 false。那么 Obj-C 中的 bool 又是什么呢?
我们知道,Obj-C 是 C 语言的超集,因此其中的 bool 其实来自于 stdbool.h 头文件中对 _Bool 的宏定义。只是在 Obj-C 中,我们无需再手动引入该头文件,因为其已经间接被 CoreFoundation.h - Foundation.h 引入。
而在 Obj-C++ 中,情况变得有些不同。按照 stdbool.h 中的定义,如果 __cplusplus 被定义了,则通常不再宏定义 bool、true 和 false,从而避免覆盖 C++ 中布尔类型 bool。
#import "Foo.h"
@implementation Foo
+ (void)foo {
// Foo.m 时,报错:Use of undeclared identifier '__cplusplus'
// Foo.mm 时,可以正常编译运行,默认输出结果为 201402(Xcode 11.5 中默认为 C++14);
// 当更改 Build Settings - Apple Clang - Language - C++ - C++ Language Dialect 为 C++98 时,
// 输出为 199711
NSLog(@"%ld", __cplusplus);
}
@end
⚠️ 注意:
由于 C 和 C++ 的代码可以较为容易地相互引入、使用、并编译,两种相似类型的二进制兼容问题就变得尤为重要和棘手。虽然
stdbool.h中的宏定义能够解决一部分二进制兼容问题,但宏定义仅作用于编译阶段。如果我们使用 C 编译器已经编译好的代码库,暴露给 C++ 代码使用并由 C++ 编译器编译(或反之),则仍然可能出现二进制兼容的问题。因此我们要尽量保证一致性,或者使用int等兼容类型替代。关于两者兼容的问题,也可以在 StackOverflow 中的 _Bool and bool: How do I solve the problem of a C library that uses _Bool? 问题中讨论。
BOOL
BOOL 是 Obj-C 中的布尔类型,但其本质是来自于宏定义:
// usr/include - objc - objc.h
/// Type to represent a boolean value.
#if defined(__OBJC_BOOL_IS_BOOL)
// Honor __OBJC_BOOL_IS_BOOL when available.
# if __OBJC_BOOL_IS_BOOL
# define OBJC_BOOL_IS_BOOL 1
# else
# define OBJC_BOOL_IS_BOOL 0
# endif
#else
// __OBJC_BOOL_IS_BOOL not set.
# if TARGET_OS_OSX || TARGET_OS_MACCATALYST || ((TARGET_OS_IOS || 0) && !__LP64__ && !__ARM_ARCH_7K)
# define OBJC_BOOL_IS_BOOL 0
# else
# define OBJC_BOOL_IS_BOOL 1
# endif
#endif
#if OBJC_BOOL_IS_BOOL
typedef bool BOOL;
#else
# define OBJC_BOOL_IS_CHAR 1
typedef signed char BOOL;
// BOOL is explicitly signed so @encode(BOOL) == "c" rather than "C"
// even if -funsigned-char is used.
#endif
#define OBJC_BOOL_DEFINED
#if __has_feature(objc_bool)
#define YES __objc_yes
#define NO __objc_no
#else
#define YES ((BOOL)1)
#define NO ((BOOL)0)
#endif
根据宏定义,当目标平台为 macOS、Mac Catalyst 或 32 位 iOS 时,BOOL 为 signed char;当目标平台为 64 位 iOS、tvOS、或 watchOS 时,BOOL 为 bool(即 _Bool)。因此在使用时,我们也要务必注意这些差异:
#import "Foo.h"
@implementation Foo
+ (BOOL)booleanValue1 {
// 当 BOOL 实际为 signed char 时,其行为将不同于 C 语言中的 _Bool 以及 C++ 中的 bool;
// 由于 signed char 大小为 1 个字节,取值范围为 [-128, 127](换算二进制为 1000,0000~0111,1111)
// 因此只要当二进制后 8 位为 0 时,比如 0001,0000,0000,高位都将被截断(丢失高位)为 0,即逻辑假
printf("%lu\n", sizeof(signed char)); // 1
printf("%lu\n", sizeof(BOOL)); // 1
// macOS Warning: Implicit conversion from constant value 256 to 'BOOL'; the only well defined values for 'BOOL' are YES and NO
return 256;
}
+ (BOOL)booleanValue2 {
return 0;
}
+ (BOOL)booleanValue3 {
return 1;
}
+ (bool)booleanValue4 {
// bool 则本质为 _Bool,因此该函数在所有平台下均返回 true
return 256;
}
+ (BOOL)booleanValue5 {
return !!256;
}
+ (void)bar {
NSLog(@"%@", [self booleanValue1] ? @"YES" : @"NO");
NSLog(@"%@", [self booleanValue2] ? @"YES" : @"NO");
NSLog(@"%@", [self booleanValue3] ? @"true" : @"false");
NSLog(@"%@", [self booleanValue4] ? @"YES" : @"NO");
NSLog(@"%@", [self booleanValue5] ? @"YES" : @"NO");
}
@end
// macOS OUTPUT:
// NO
// NO
// true
// YES
// YES
// iOS ARM64 OUTPUT:
// YES
// NO
// true
// YES
// YES
BOOL 中对应的逻辑是 YES 为真,NO 为假,其本质分别即 __objc_yes 和 __objc_no:
// 摘自上文
//...
// __has_feature 可以用来检查编译器是否包含某个功能,以区分针对不同编译器的实现
#if __has_feature(objc_bool)
#define YES __objc_yes
#define NO __objc_no
#else
#define YES ((BOOL)1)
#define NO ((BOOL)0)
而 __objc_yes 与 __objc_no 的本质,我们可以在 LLVM 官网的《Objective-C 字面量》文档中找到:
The compiler implicitly converts
__objc_yesand__objc_noto(BOOL)1and(BOOL)0. The keywords are used to disambiguateBOOLand integer literals.编译器隐式将
__objc_yes转换为(BOOL)1,将__objc_no转换为(BOOL)0。这些关键字是用来区分BOOL与整型字面量的。—— Objective-C Literals
__NSCFBoolean 与 CFBoolean
使用 NSUserDefaults 使得我们可以很容易持久化一些值,这里我们将 BOOL 的 YES 保存,并尝试取出:
[[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] setBool:YES forKey:@"BOOL_YES"];
// [[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] setObject:@YES forKey:@"BOOL_YES"];
// [[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] setObject:@(YES) forKey:@"BOOL_YES"];
// - (id)valueForKey:(NSString *)key;
id boolYes = [[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] valueForKey:@"BOOL_YES"];
NSLog(@"%@", [boolYes class]);
// __NSCFBoolean
// (lldb) p [boolYes superclass]
(// Class) $0 = NSNumber
由于 valueForKey: 是一个返回 id 类型的方法,此时我们发现 boolYes 的类是 __NSCFBoolean,父类为 NSNumber。__NSCFBoolean 的本质是桥接 CoreFoundation 中的 CFBoolean。
CFBoolean objects are used to wrap boolean values for use in Core Foundation property lists and collection types.
CFBoolean 对象包装了布尔值,用在 CoreFoundation 中的属性列表和集合类型。
—— CFBoolean, Apple Documentation
CFBoolean 中真值为 kCFBooleanTrue,假值为 kCFBooleanFalse:
// CoreFoundation - CFNumber.h
typedef const struct CF_BRIDGED_TYPE(NSNumber) __CFBoolean * CFBooleanRef;
CF_EXPORT
const CFBooleanRef kCFBooleanTrue;
CF_EXPORT
const CFBooleanRef kCFBooleanFalse;
CF_EXPORT
CFTypeID CFBooleanGetTypeID(void);
CF_EXPORT
Boolean CFBooleanGetValue(CFBooleanRef boolean);
Boolean 与 boolean_t
// usr/include - MacTypes.h
/********************************************************************************
Boolean types and values
Boolean Mac OS historic type, sizeof(Boolean)==1
bool Defined in stdbool.h, ISO C/C++ standard type
false Now defined in stdbool.h
true Now defined in stdbool.h
*********************************************************************************/
typedef unsigned char Boolean;
Boolean 在 Obj-C 中是一个并不常用的类型。根据头文件,其来源于 macOS 历史遗留,实际类型为 unsigned char。
// usr/include - mach - i386 - boolean.h
/*
* File: boolean.h
*
* Boolean type, for I386.
*/
#ifndef _MACH_I386_BOOLEAN_H_
#define _MACH_I386_BOOLEAN_H_
#if defined(__x86_64__) && !defined(KERNEL)
typedef unsigned int boolean_t;
#else
typedef int boolean_t;
#endif
#endif /* _MACH_I386_BOOLEAN_H_ */
boolean_t 也不常用,根据头文件,当目标平台为 x86_64 架构时,其相当于 unsigned int,反之则为 int。
printf("%lu\n", sizeof(Boolean));
printf("%lu\n", sizeof(boolean_t));
// 1
// 4
Boolean 和 boolean_t 分别占用 1 个和 4 个字节(该大小不区分目标平台)。而在日常开发中,由于我们几乎很少会使用到这两个类型,故本文不再赘述。
DYLD_BOOL
DYLD_BOOL 在平时我们也不常用,其本质是来自于 dyld.h 中的一个枚举类型,其中 TRUE 为 1,FALSE 为 0:
// usr/include - mach-o - dyld.h
#ifndef ENUM_DYLD_BOOL
#define ENUM_DYLD_BOOL
#undef FALSE
#undef TRUE
enum DYLD_BOOL { FALSE, TRUE };
#endif /* ENUM_DYLD_BOOL */
逻辑表达式
在开发过程中,另一个离不开逻辑判断的地方是逻辑表达式。在这些表达式中,我们通常会使用 &&、||、==、!=、! 等逻辑运算符。那么它们的返回值是什么类型呢?
为了避免编译器进行类型转换,这里使用了 __auto_type 来代表表达式的返回类型,并通过打断点查看逻辑表达式的返回值类型:
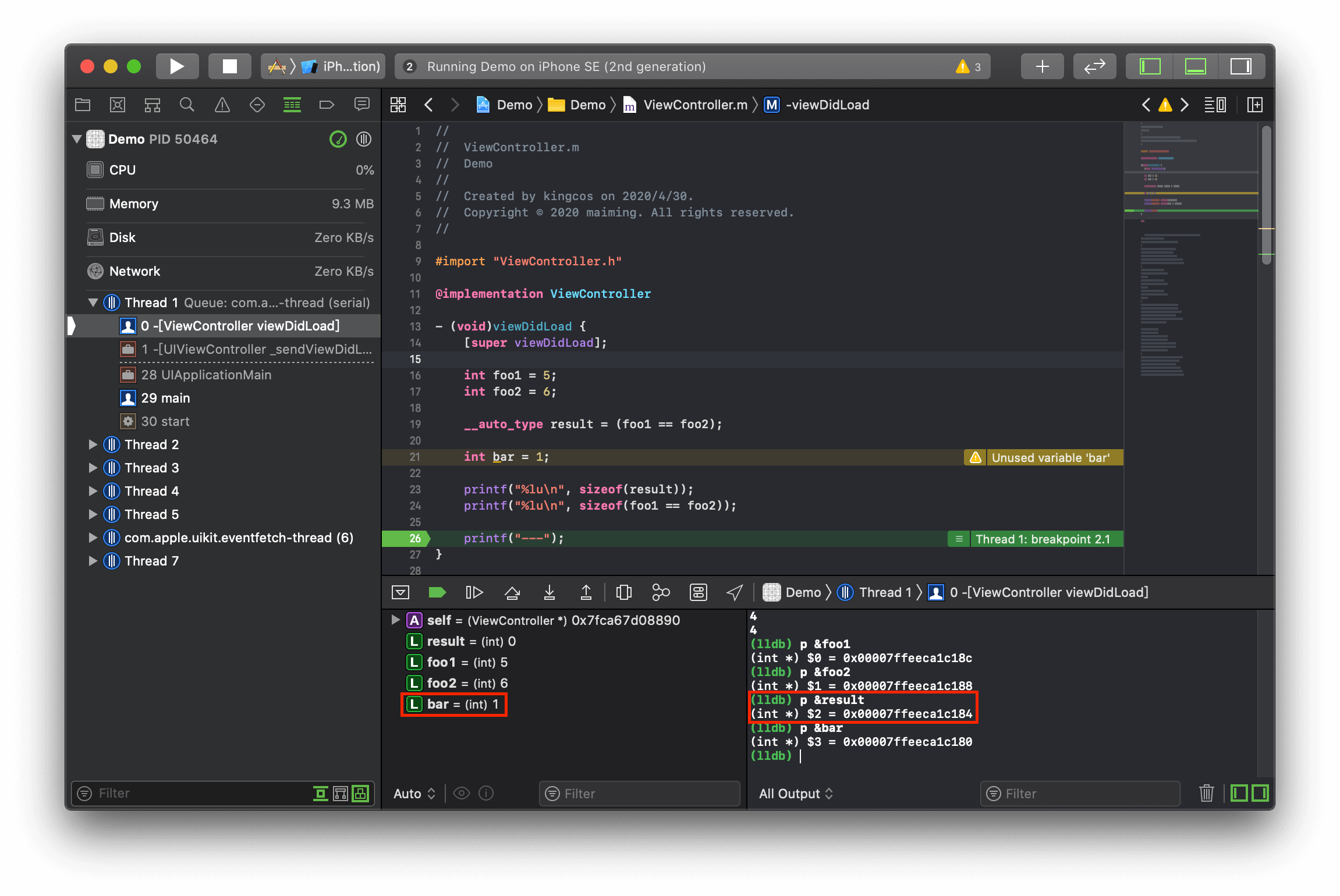
__auto_type在 Swift 中,我们已经习惯于编译器自动进行的类型推断。而 GCC 4.9 为 C 语言引入了
__auto_type关键字,用处主要在于一些宏定义中能够实现「类型推断」,类似 C++ 中的auto。LLVM 中也加入了该关键字。#if defined(__cplusplus) #define let auto const #else #define let const __auto_type #endif #if defined(__cplusplus) #define var auto #else #define var __auto_type #endif
我们也可以通过 Xcode Menu - Debug - Debug Workflow - View Memory 查看变量的实际内存占用:
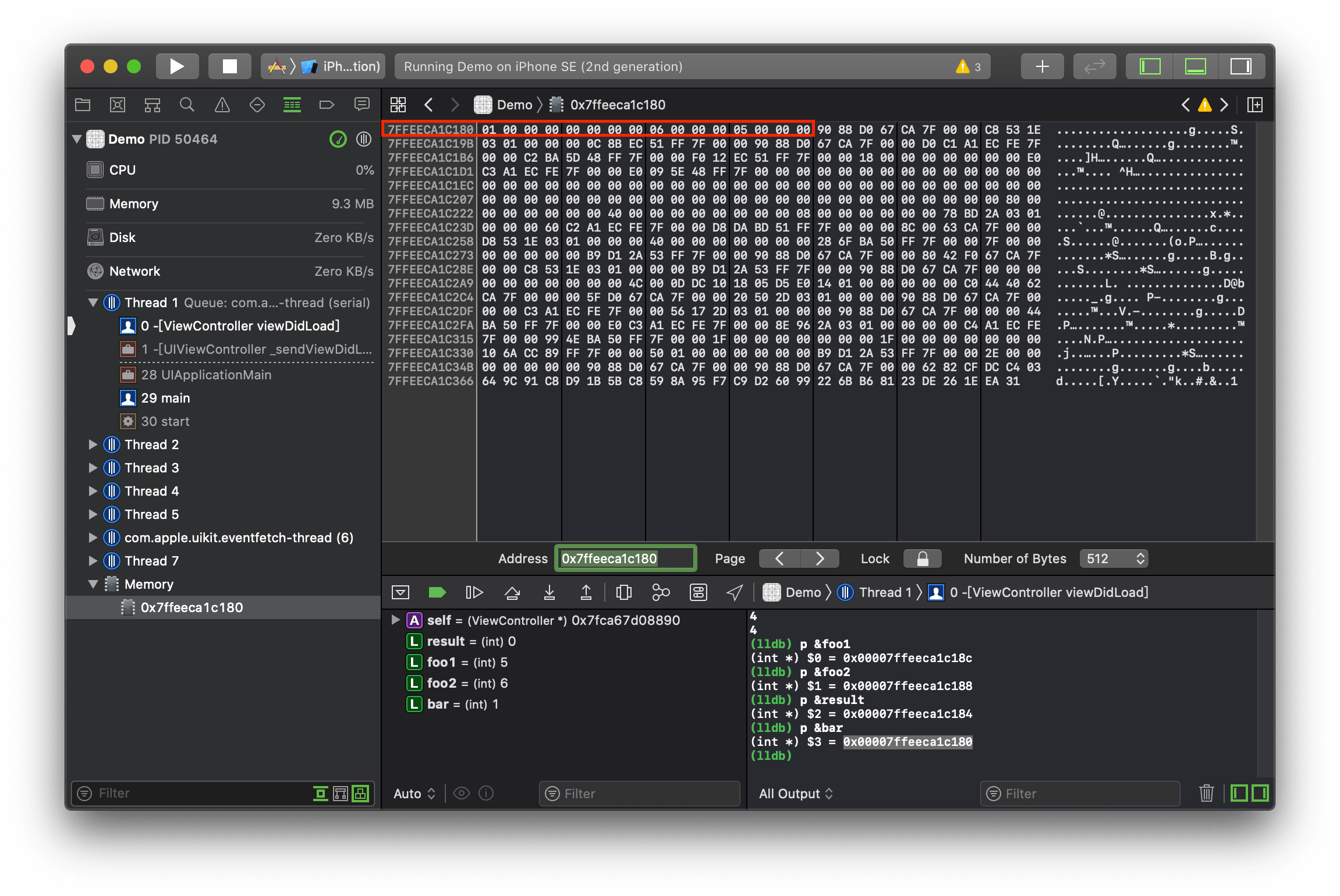
最终我们可以确定逻辑表达式的返回值类型其实是 int,占用 4 个字节。我们也可以在 C99 标准中找到以下说明来佐证:
The
==(equal to) and!=(not equal to) operators are analogous to the relational operators except for their lower precedence. Each of the operators yields 1 if the specified relation is true and 0 if it is false. The result has typeint. For any pair of operands, exactly one of the relations is true.
==(等于)和!=(不等于)运算符与关系运算符类似,只是它们的优先级较低。如果指定的关系为真,运算符会返回 1,如果为假,则返回 0。结果类型为int。对于任何一项(判等)操作,都必有一个关系为真。—— C99 §6.5.9.3
Conclusion
| 类型 | 底层类型 | 头文件 | sizeof | 真值 | 假值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| _Bool (C) | unsigned int | stdbool.h | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| bool (C) | _Bool (C) | stdbool.h | 1 | true | false |
| bool (C++) | - | - | 1 | true | false |
| BOOL (Obj-C) |
macOS/iOS 32bit signed char iOS 64bit: _Bool |
objc.h | 1 | YES | NO |
| BOOL (Obj-C++) |
macOS/iOS 32bit: signed char iOS 64bit: bool(C++) |
objc.h | 1 | YES | NO |
| __NSCFBoolean | CFBoolean | - | - | @YES | @NO |
| CFBooleanRef | CFBoolean | CFNumber.h | 8 | kCFBooleanTrue | kCFBooleanFalse |
| Boolean | unsigned char | MacTypes.h | 1 | - | - |
| boolean_t | x86_64: unsigned int others: int |
boolean.h | 4 | - | - |
| DYLD_BOOL | enum DYLD_BOOL | dyld.h | 4 | TRUE (1) | FALSE (0) |
Reference
- BOOL / bool / Boolean / NSCFBoolean - by Mattt
- C99 Standard PDF - open-std.org
- _Bool data type of C99 - StackOverflow
- _Bool and bool: How do I solve the problem of a C library that uses _Bool? - StackOverflow
- Boolean data type - Wikipedia
- BOOL - Apple Documentation
- Objective-C Literals - LLVM.org
- CFBoolean - Apple Documentation
- CF Source Browser - Apple Opensource
- Referring to a Type with typeof - GCC
- Add support for GCC’s ‘__auto_type’ extension. - LLVM
