| Date | Notes |
|---|---|
| 2019-06-14 | 增加 man nm 截图 |
| 2019-04-29 | 完善 @package |
| 2019-03-30 | gcc, clang; macOS 10.14.2 |
| 2020-01-17 | 勘误,部分细节调整 |
Preface
Obj-C 中的实例变量,即 Instance Variables,简称为 ivar。在面向对象的概念中,一个类的对外暴露决定了其所提供的能力,对子类则需要提供一定的扩展性,但有些时候我们不希望外界甚至子类知道一些细节,这时就用到了访问控制(Access Control)。在 C++、Java、Swift 等大多数高级语言中都有这样的概念,那么这次就来谈谈 Obj-C 中实例变量和类的访问控制。
访问控制修饰符
@public
@interface Foo : NSObject {
@public
NSString *_ivar;
}
@end
@implementation Foo
@end
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
Foo *f = [[Foo alloc] init];
f->_ivar = @"kingcos.me";
NSLog(@"%@", f->_ivar);
return 0;
}
// OUTPUT:
// kingcos.me
声明为 @public 的实例变量是访问控制中开放范围最广的,其允许外界可以直接访问(当然,前提是引入包含该声明的头文件)。
@protected
@interface SubFoo : Foo {
NSString *_ivar2;
@protected
NSString *_ivar3;
}
- (void)subFooFunc;
@end
@implementation SubFoo
- (void)subFooFunc {
self->_ivar2 = @"kingcos.me";
self->_ivar3 = @"kingcos.me";
NSLog(@"%@", self->_ivar2);
NSLog(@"%@", self->_ivar3);
}
@end
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
SubFoo *f = [[SubFoo alloc] init];
// ERROR: Instance variable '_ivar2' is protected
// f->_ivar2 = @"kingcos.me";
[f subFooFunc];
return 0;
}
// OUTPUT:
// kingcos.me
// kingcos.me
声明为 @protected 的实例变量只能在本类、本类的分类以及子类中使用。注意,当不使用任何访问控制修饰符时,类中实例变量默认即为 @protected(注意:类扩展中是个例外,详见「类扩展」一节)。
@private
@interface Foo : NSObject {
@private
NSString *_ivar4;
}
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *prop;
- (void)fooFunc;
@end
@implementation Foo
- (void)fooFunc {
self->_ivar4 = @"kingcos.me";
self->_prop = @"kingcos.me";
NSLog(@"%@", self->_ivar4);
NSLog(@"%@", self->_prop);
}
@end
@interface Foo (Ext)
- (void)fooExtFunc;
@end
@implementation Foo (Ext)
- (void)fooExtFunc {
self->_ivar4 = @"kingcos.me";
self->_prop = @"kingcos.me";
NSLog(@"%@", self->_ivar4);
NSLog(@"%@", self->_prop);
}
@end
@interface SubFoo : Foo {
NSString *_ivar2;
@protected
NSString *_ivar3;
}
- (void)subFooFunc;
@end
@implementation SubFoo
- (void)subFooFunc {
self->_ivar2 = @"kingcos.me";
self->_ivar3 = @"kingcos.me";
NSLog(@"%@", self->_ivar2);
NSLog(@"%@", self->_ivar3);
// ERROR: Instance variable '_ivar4' is private
// self->_ivar4 = @"kingcos.me";
// ERROR: Instance variable '_prop' is private
// self->_prop = @"kingcos.me";
}
@end
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
Foo *f = [[Foo alloc] init];
[f fooFunc];
[f fooExtFunc];
SubFoo *sf = [[SubFoo alloc] init];
[sf subFooFunc];
return 0;
}
// OUTPUT:
// kingcos.me
// kingcos.me
// kingcos.me
// kingcos.me
// kingcos.me
// kingcos.me
声明为 @private 的实例变量是访问控制中开放范围最小的,只能被本类和本类的分类访问到,子类中也无法访问。在类声明中的属性(@property),系统会自动为我们创建一个 _ 开头的实例变量,这个实例变量的可见程度默认也是 @private。
@package
@package 在平时并不多见,但从 @package 能够延伸到一些其他问题。根据官方文档所述:
@packageis a new instance variable protection class, like@publicand@protected.@packageinstance variables behave as follows:
@publicin 32-bit;@publicin 64-bit, inside the framework that defined the class;@privatein 64-bit, outside the framework that defined the class.In 64-bit, the instance variable symbol for an
@packageivar is not exported, so any attempt to use the ivar from outside the framework that defined the class will fail with a link error. See “64-bit Class and Instance Variable Access Control” for more about instance variable symbols.—— @package Instance Variables, Objective-C Release Notes
译:
@package是一个新的实例变量保护类型,就像@public和@protected。@package(修饰)的实例变量行为如下:
- 在 32 位下,(等同于)
@public- 在 64 位下,且在定义该类的 Framework 中(等同于)
@public- 在 64 位下,但不在定义该类的 Framework 中(等同于)
@private—— @package 实例变量,Objective-C 发布说明
Using the modern runtime, an
@packageinstance variable has@publicscope inside the executable image that implements the class, but acts like@privateoutside.The
@packagescope for Objective-C instance variables is analogous toprivate_externfor C variables and functions. Any code outside the class implementation’s image that tries to use the instance variable gets a link error.This scope is most useful for instance variables in framework classes, where
@privatemay be too restrictive but@protectedor@publictoo permissive.—— The Scope of Instance Variables, The Objective-C Programming Language
译:
借助现代运行时,
@package实例变量在实现类的同一可执行镜像之内为@public,之外为@private。Obj-C 实例变量的
@package域类似 C 变量和函数的private_extern。任何在类实现镜像之外的代码尝试访问该类型实例变量,将发生链接错误。由于
@private太过限制,而@protected或@public又太开放,该域对于框架类中的实例变量十分有用。—— 实例变量的域,Obj-C 编程语言
尝试在原有的项目中建立一个 Cocoa Framework(Xcode 11 中为 Framework)的 Target 和一个 Static Library,并导入以下代码:
// Baz.h - Framework
// 需手动将 `Baz.h` 移动至 Bar Taget 的 Build Phases 中 Headers 的 Public 域,
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN
@interface Baz : NSObject {
@package
NSString *ivar5;
}
@end
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END
// Bar.h
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
//! Project version number for Bar.
FOUNDATION_EXPORT double BarVersionNumber;
//! Project version string for Bar.
FOUNDATION_EXPORT const unsigned char BarVersionString[];
// In this header, you should import all the public headers of your framework using statements like #import <Bar/PublicHeader.h>
#import "Baz.h"
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface StaticBar : NSObject {
@package
NSString *_ivar6;
}
@end
// StaticBar.h - Static Library
// 需手动在主 Target 的 Build Phases 中 Link Binary With Libraries 中添加 libStaticBar.a
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface StaticBar : NSObject {
@package
NSString *_ivar6;
}
@end
// main.m
#import <Bar/Bar.h>
#import "StaticBar.h"
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
Baz *b = [[Baz alloc] init];
// ERROR: Undefined symbol: _OBJC_IVAR_$_Baz.ivar5
// b->ivar5 = @"kingcos.me";
StaticBar *sb = [[StaticBar alloc] init];
sb->_ivar6 = @"kingcos.me";
NSLog(@"%@", sb->_ivar6);
return 0;
}
// OUTPUT:
// kingcos.me
尝试发现:
- 当 Framework 的 Mach-O Type 为动态库(Dynamic Library)时,将出现错误,即无法访问到
@package修饰的_name实例变量; - 当使用 Static Library 或 Framework 的 Mach-O Type 为静态库(Static Library)或时,可以正常编译并运行。
这其实也就验证了官方文档中对于 @private 在镜像(Image)的描述。对于静态库,其在编译时刻即被载入,因此属于同一个镜像,可以正常编译并运行;而动态库只有在运行时才能被载入,并不是同一个镜像,因此访问时出现了链接错误。在 StackOverflow 上的一个问题中也提到了 Image(镜像),相关链接可在文末「Reference」中找到。
《iOS 中的库与框架》一文。
类扩展
在 Obj-C 的类扩展(Class Extension)中,我们可以定义一些不想暴露在外界(.h)的实例变量、属性、或方法,做到「物理」隔离。需要注意的是,定义在类扩展中的实例变量,默认为 @private,仅供本类使用:
// Foo.h
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN
@interface Foo : NSObject
@end
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END
// Foo+Private.h
#import "Foo.h"
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN
@interface Foo () {
int _ivar2;
@public
int _ivar3;
}
@end
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END
// Foo.m
#import "Foo.h"
#import "Foo+Private.h"
@interface Foo () {
int _ivar1;
}
@end
@implementation Foo
- (void)foo {
NSLog(@"%d", self->_ivar1);
NSLog(@"%d", self->_ivar2);
NSLog(@"%d", self->_ivar3);
}
@end
// SubFoo.h
#import "Foo.h"
#import "Foo+Private.h"
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN
@interface SubFoo : Foo
@end
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END
// SubFoo.m
#import "SubFoo.h"
@implementation SubFoo
- (void)subFoo {
// ERROR: 'SubFoo' does not have a member named '_ivar1'
// NSLog(@"%d", self->_ivar1);
// ERROR: Instance variable '_ivar2' is private
// NSLog(@"%d", self->_ivar2);
NSLog(@"%d", self->_ivar3);
}
@end
如上,对外我们只需要暴露 Foo.h,而将类扩展所在的 Foo+Private.h 不暴露为 Public Header 即可;或者也可以将类扩展直接定义在 .m 中。而由于类扩展属于编译时刻的语法,因此其定义务必要在本类的 @implementation 之前,切忌在分类实现文件中定义的类扩展中增加实例变量(此时增加属性也不会自动生成实例变量)。
符号(Symbols)
nm 是 macOS 自带的命令行程序,可以用来查看 Mach-O 文件的 LLVM 符号表,但默认情况将打印全部的符号,如果希望只显示外部的全局符号,可以使用 -g 参数:
// main.m
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface Computer : NSObject {
int _memorySize;
@public
NSString *_name;
@package
NSString *_macAdress;
@protected
int _diskSize;
@private
int _secret;
}
@property(nonatomic, copy) NSString *arch;
@end
@implementation Computer
@end
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
return 0;
}
// nm executable-mach-o-file
// 0000000100000e00 t -[Computer .cxx_destruct]
// 0000000100000d90 t -[Computer arch]
// 0000000100000dc0 t -[Computer setArch:]
// 0000000100001270 S _OBJC_CLASS_$_Computer
// U _OBJC_CLASS_$_NSObject
// 0000000100001218 s _OBJC_IVAR_$_Computer._arch
// 0000000100001238 S _OBJC_IVAR_$_Computer._diskSize
// 0000000100001220 s _OBJC_IVAR_$_Computer._macAdress
// 0000000100001230 S _OBJC_IVAR_$_Computer._memorySize
// 0000000100001240 s _OBJC_IVAR_$_Computer._secret
// 0000000100001228 S _OBJC_IVAR_$_Computer._name
// 0000000100001248 S _OBJC_METACLASS_$_Computer
// U _OBJC_METACLASS_$_NSObject
// 0000000100000000 T __mh_execute_header
// U __objc_empty_cache
// 0000000100000e70 T _main
// U _objc_getProperty
// U _objc_msgSend
// U _objc_setProperty_nonatomic_copy
// U _objc_storeStrong
// U dyld_stub_binder
// nm -g executable-mach-o-file
// 0000000100001270 S _OBJC_CLASS_$_Computer
// U _OBJC_CLASS_$_NSObject
// 0000000100001238 S _OBJC_IVAR_$_Computer._diskSize
// 0000000100001230 S _OBJC_IVAR_$_Computer._memorySize
// 0000000100001228 S _OBJC_IVAR_$_Computer._name
// 0000000100001248 S _OBJC_METACLASS_$_Computer
// U _OBJC_METACLASS_$_NSObject
// 0000000100000000 T __mh_execute_header
// U __objc_empty_cache
// 0000000100000e70 T _main
// U _objc_getProperty
// U _objc_msgSend
// U _objc_setProperty_nonatomic_copy
// U _objc_storeStrong
// U dyld_stub_binder
在 64 位的 Obj-C 中,每个类以及实例变量的访问控制都有一个与之关联的符号,类或实例变量都会通过引用此符号来使用。类符号的格式为 _OBJC_CLASS_$_ClassName 和 _OBJC_METACLASS_$_ClassName,实例变量符号的格式为 _OBJC_IVAR_$_ClassName.IvarName。
在 C/C++ 中也有类似的符号概念。
可见程度(Visibility)
在不明确指定的默认情况下,这些符号均是暴露给外界的。但 gcc 编译器都可以通过 -fvisibility 参数设定可见程度,但优先级低于直接在源代码中声明可见程度。-fvisibility=default 即默认可见程度,-fvisibility=hidden,使得编译源文件内未明确指定的符号隐藏。
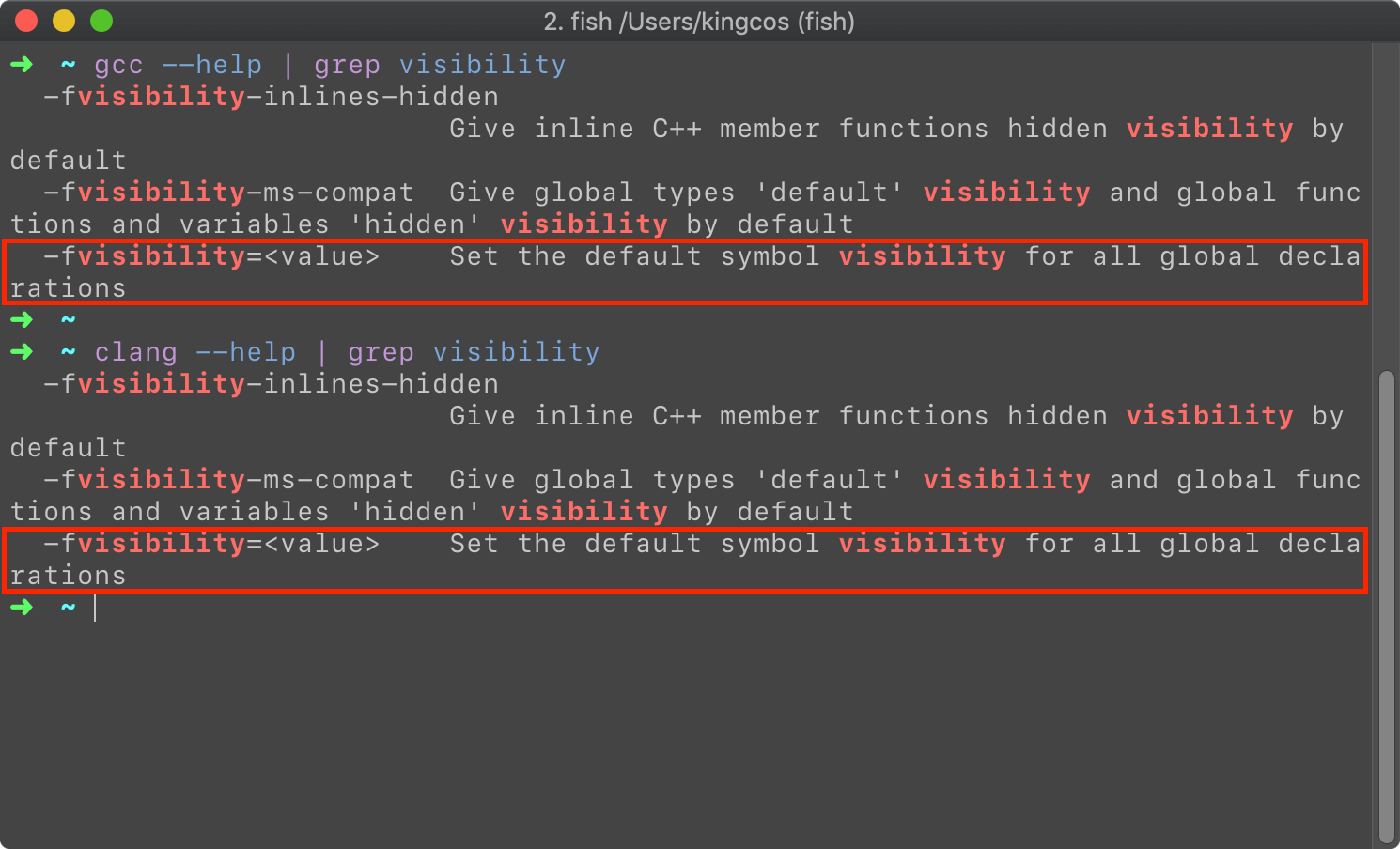
虽然看似 clang 也支持该参数,但在测试中,本机的 clang 却无法达到和 gcc 同样的效果。
建立一个 Test.cpp 的 C++ 源文件,但在文件内部不进行任何的可见程度设定,建立 main.cpp 并在主函数中调用 Test 中的方法。我们将先把 Test.cpp 编译并打包为静态库文件,再用 main.cpp 编译好的目标文件将其链接起来:
// Test.cpp
#include <stdio.h>
void test() {
printf("Test");
}
// main.cpp
void test();
int main() {
test();
}
// gcc:
// ➜ ~ g++ -shared -o libTest.so Test.cpp
// ➜ ~ g++ -o main main.cpp -L ./ -lTest
// ➜ ~ ./main
// Test⏎
// clang:
// ➜ ~ clang++ -c Test.cpp
// ➜ ~ ar -r libTest.a Test.o
// ar: creating archive libTest.a
// ➜ ~ clang++ -c main.cpp
// ➜ ~ clang++ main.o -L. -lTest -o main
// ➜ ~ ./main
// Test⏎
使用 nm 查看其符号表,注意:C++ 中的符号在使用时是解码过的,所以默认输出也是解码后的符号,我们可以使用 -C 参数限制其解码,-C 与 -g 一起可以直接使用 -gC。
// gcc
// ➜ ~ nm libTest.so
// 0000000000000f70 T __Z4testv
// U _printf
// U dyld_stub_binder
// ➜ ~ nm -gC libTest.so
// 0000000000000f70 T test()
// U _printf
// U dyld_stub_binder
// ➜ ~ nm -gC main
// U test()
// 0000000100000000 T __mh_execute_header
// 0000000100000f80 T _main
// U dyld_stub_binder
保持源代码文件不更改,添加编译参数为 -fvisibility=hidden,则将出现链接错误:
// gcc:
// ➜ ~ g++ -shared -o libTest.so -fvisibility=hidden Test.cpp
// ➜ ~ g++ -o app main.cpp -L ./ -lTest
// Undefined symbols for architecture x86_64:
// "test()", referenced from:
// _main in main-0369ae.o
// ld: symbol(s) not found for architecture x86_64
// clang: error: linker command failed with exit code 1 (use -v to see invocation)
//➜ ~ nm -gC libTest.so
// U _printf
// U dyld_stub_binder
在 C/C++源文件中,也可以通过 __attribute((visibility("value"))) 设定某个方法或类的可见程度。尝试将 Test.cpp 的 test() 方法设置为 hidden,也将出现链接错误:
// Test.cpp
#include <stdio.h>
__attribute((visibility("hidden")))
void test() {
printf("Test");
}
// gcc:
// ➜ ~ g++ -shared -o libTest.so Test.cpp
// ➜ ~ g++ -o app main.cpp -L ./ -lTest
// Undefined symbols for architecture x86_64:
// "test()", referenced from:
// _main in main-45a3c6.o
// ld: symbol(s) not found for architecture x86_64
// clang: error: linker command failed with exit code 1 (use -v to see invocation)
// ➜ ~ nm libTest.so
// U _printf
// U dyld_stub_binder
__attribute__((visibility("hidden")))
@interface ClassName : SomeSuperclass
官方文档中提到,在 Obj-C 中可以通过 __attribute__((visibility("hidden"))) 来设定类的可见程度,但关于这点我并没有实践成功,尝试将代码翻译为 C++,但似乎并有因为该语句而增加有用的信息。但在 objc-api.h 中有针对默认可见程度 __attribute__((visibility("default"))) 的宏定义,它被定义为一个更简单使用的宏 OBJC_VISIBLE(当然,该宏在 Win 32 系统中代表 __declspec(dllexport) 或 __declspec(dllimport))。
// objc-api.h
#if !defined(OBJC_VISIBLE)
# if TARGET_OS_WIN32
# if defined(BUILDING_OBJC)
# define OBJC_VISIBLE __declspec(dllexport)
# else
# define OBJC_VISIBLE __declspec(dllimport)
# endif
# else
# define OBJC_VISIBLE __attribute__((visibility("default")))
# endif
#endif
Reference
- The Objective-C Programming Language - Apple
- Objective-C Release Notes - Apple
- 64-bit Class and Instance Variable Access Control - Apple
- What does the @package directive do in Objective-C? - StackOverflow
- GCC 系列:
__attribute__((visibility("")))- veryitman - nm 命令 - IBM
- Attributes in Clang - LLVM.org
- iOS 中的库与框架 - kingcos
- 巧用 Class Extension 分离接口依赖 - sunnyxx
