| Date | Notes | Source Code | Demo |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019-04-16 | 优化结构 | - | - |
| 2019-04-13 | 首次提交 | objc4-750、xnu-4903.221.2 | Category in iOS |
| 2019-10-23 | 添加首图,细节微调 | - | - |
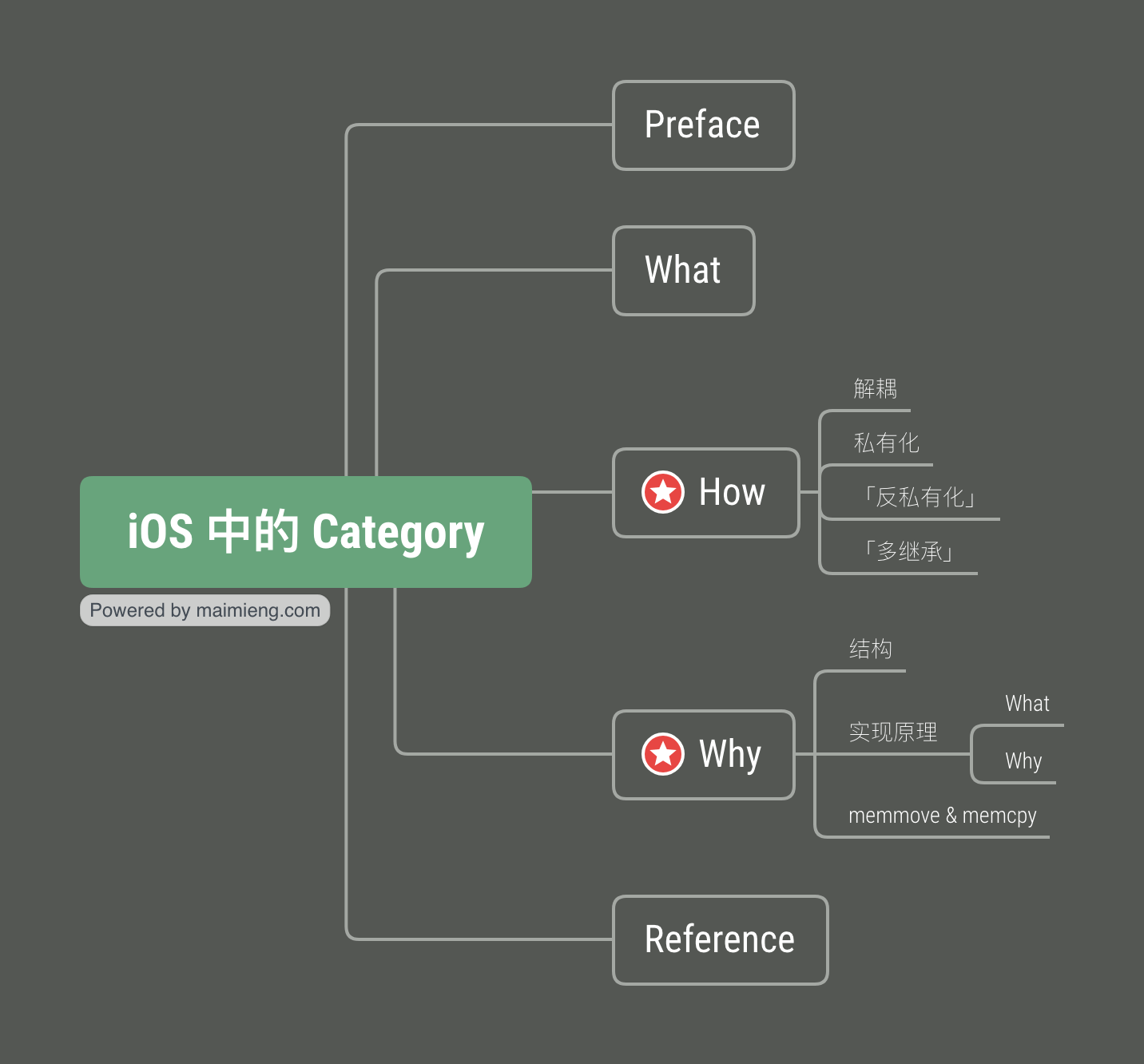
Preface
iOS 中的 Category 中文常译作分类、类别(为表述统一,本文将使用 Category 特指该技术)。我们经常会使用 Category 来对一个类进行扩展,使得在不破坏主类结构的同时可以具备更多的功能;也可以使用 Category 对一个类进行拆分,使得其结构更加清晰条理。本文将从 What - How - Why 谈谈 iOS 中 Category。
What
什么是 Category 呢?
Category 是 Obj-C 语言中所提供的一项功能,它可以为 Obj-C 类添加额外的属性、方法,也可以遵守其他协议。
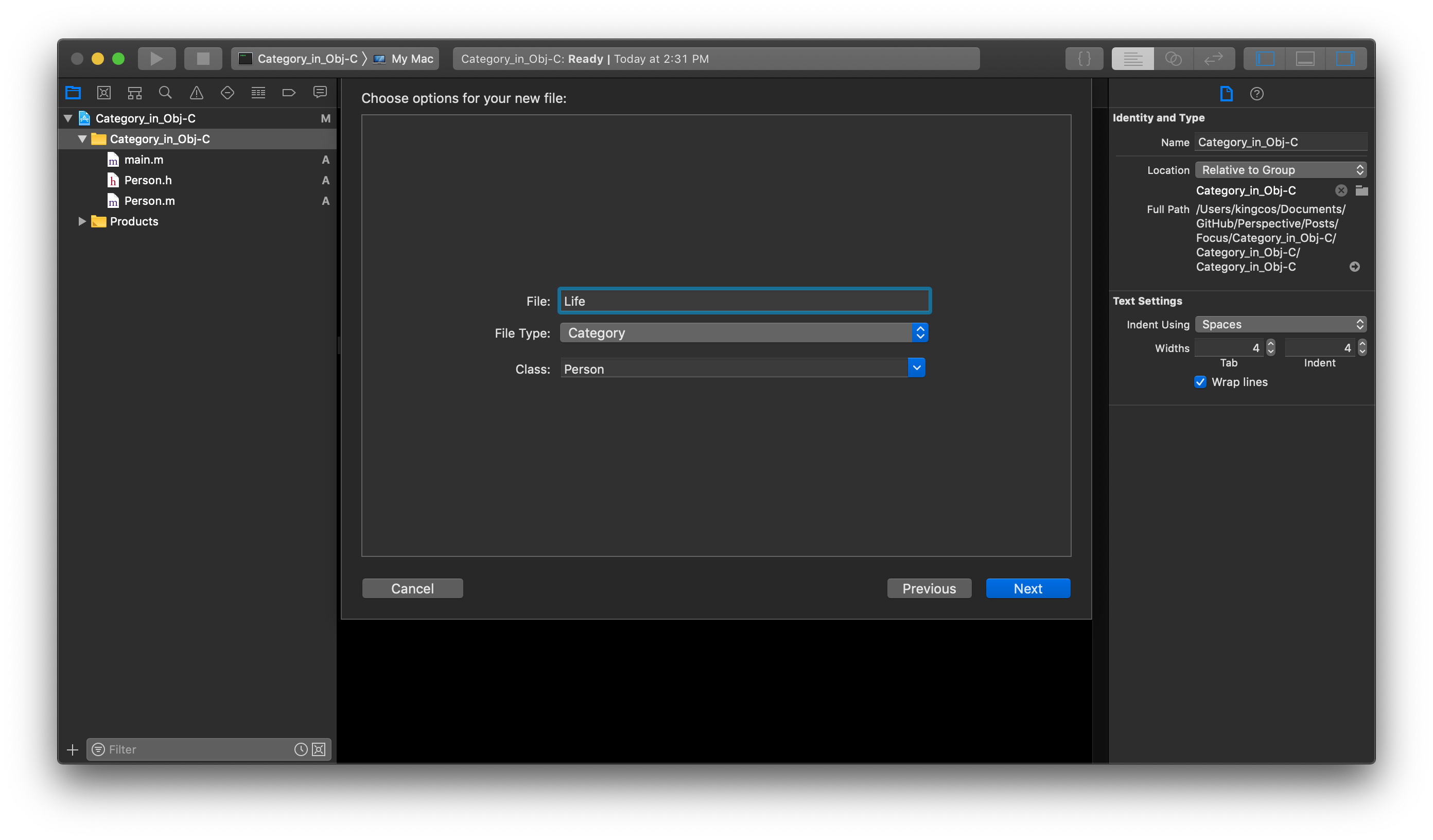
Xcode 中已经为 Category 已经提供了模版来建立,只需要指定 Category 的名称以及被添加 Category 类名即可。当然,我们也可以手动来自己建立,Category 的语法与类的声明与实现比较类似:
@interface Foo (Bar) <SomeProtocol>
- (void)foo;
@end
@implementation Foo (Bar)
- (void)foo {}
- (void)someMethodFromProtocol {}
@end
How
Category 通常都有哪些用处呢?
解耦
假如有一个人(Person),他需要工作(Work)和生活(Life),而工作和生活所做的事情显然是不一样的,那么我们就可以使用 Category 将人的这它们进行解耦:
@interface Person
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
@end
@implementation Person
@end
// ---
@interface Person (Life)
- (void)playWithPet;
@end
@implementation Person (Life)
- (void)playWithPet {}
@end
// ---
@interface Person (Work)
- (void)codeForWork;
@end
@implementation Person (Work)
- (void)codeForWork {}
@end
这样,Person+Life 中可以定义与生活相关的方法,而 Person+Work 中将专注于工作。当人需要运动(Sports)时,只需要再为 Person 添加 Person+Sports 的 Category 即可,这并不需要改动主类本身从而实现了解耦。
私有化
使用 Xcode 模版新建 Category 后,将会自动创建两个文件:ClassName+CategoryName.h & ClassName+CategoryName.m。当我们不希望某个 Category 可以在外界访问时,只需要不把它作为公共头文件(Public Header)暴露出去即可,即实现了私有化。需要注意的是,同样可以实现私有化的方案是使用类扩展(Class Extension),其因语法相似但没有定义名称被很多人称为「匿名分类(Category)」。不过本质上说,Category 和类扩展是完全不同的:
// Class Extension
@interface Person ()
- (void)secret;
@end
类扩展是可以定义在单独的 .h 或者 .m 中,其主要可以使得外界无法直接访问到定义的成员变量、属性或方法。关于类扩展与访问控制,可详见《Obj-C 中成员变量和类的访问控制》一文。
「反私有化」
Category 不仅可以私有化,其实也可以「反私有化」。如果我们希望调用一个没有声明的方法,此时就可以在其 Category 或者类扩展中声明该方法,再进行调用。当然,Obj-C 中方法调用本质是消息发送,只要我们知道了消息的发送者和接收者,即使没有声明也总有方法来发送消息。
「多继承」
因为 Category 是支持遵守协议(Protocol)的,那么不同的 Category 就可以遵守不同的协议,实现类似「多继承」的特性。但为什么是加引号的「多继承」呢?因为这样的协议遵守只能获得方法的声明,却无法获得父类的具体实现。
@protocol LifeProtocol <NSObject>
- (void)playWithPet;
@end
@interface Person (Life) <LifeProtocol>
@end
@implementation Person (Life)
- (void)playWithPet {}
@end
// ---
@protocol WorkProtocol <NSObject>
- (void) workHard;
@end
@interface Person (Work) <WorkProtocol>
@end
@implementation Person (Work)
- (void)workHard {}
@end
Why
Obj-C 中的 Category 底层是如何实现的呢?
结构
// Person+Life.h
/**
LifeProtocol
*/
@protocol LifeProtocol <NSObject>
- (void)eat;
@end
/**
Person+Life
*/
@interface Person (Life) <LifeProtocol>
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
// Instance method
- (void)run;
// Class method
+ (void)foo;
// Protocol method
- (void)eat;
@end
定义一个完整的 Person 类,它遵守了协议,存储了属性,并定义实现了对象方法和类方法。为了便于下面的分析,我们使用 xcrun -sdk iphoneos clang -arch arm64 -rewrite-objc Person+Life.m 命令将 Person+Life.m 翻译为 C/C++ 代码(Person+Life.cpp),关于翻译 Obj-C 代码的细节,可详见《将 Obj-C 代码翻译为 C++ 代码》一文。
// Person+Life.cpp
struct _category_t {
const char *name; // 类名
struct _class_t *cls; // 类指针
const struct _method_list_t *instance_methods; // 对象方法列表指针
const struct _method_list_t *class_methods; // 类方法列表指针
const struct _protocol_list_t *protocols; // 协议列表指针
const struct _prop_list_t *properties; // 属性列表指针
};
static struct _category_t _OBJC_$_CATEGORY_Person_$_Life __attribute__ ((used, section ("__DATA,__objc_const"))) =
{
"Person",
0, // &OBJC_CLASS_$_Person,
(const struct _method_list_t *)&_OBJC_$_CATEGORY_INSTANCE_METHODS_Person_$_Life,
(const struct _method_list_t *)&_OBJC_$_CATEGORY_CLASS_METHODS_Person_$_Life,
(const struct _protocol_list_t *)&_OBJC_CATEGORY_PROTOCOLS_$_Person_$_Life,
(const struct _prop_list_t *)&_OBJC_$_PROP_LIST_Person_$_Life,
};
// 对象方法列表
static struct /*_method_list_t*/ {
unsigned int entsize; // sizeof(struct _objc_method)
unsigned int method_count;
struct _objc_method method_list[2];
} _OBJC_$_CATEGORY_INSTANCE_METHODS_Person_$_Life __attribute__ ((used, section ("__DATA,__objc_const"))) = {
sizeof(_objc_method),
2,
{{(struct objc_selector *)"run", "v16@0:8", (void *)_I_Person_Life_run},
{(struct objc_selector *)"eat", "v16@0:8", (void *)_I_Person_Life_eat}}
};
// 类方法列表
static struct /*_method_list_t*/ {
unsigned int entsize; // sizeof(struct _objc_method)
unsigned int method_count;
struct _objc_method method_list[1];
} _OBJC_$_CATEGORY_CLASS_METHODS_Person_$_Life __attribute__ ((used, section ("__DATA,__objc_const"))) = {
sizeof(_objc_method),
1,
{{(struct objc_selector *)"foo", "v16@0:8", (void *)_C_Person_Life_foo}}
};
// 协议列表
static struct /*_protocol_list_t*/ {
long protocol_count; // Note, this is 32/64 bit
struct _protocol_t *super_protocols[1];
} _OBJC_CATEGORY_PROTOCOLS_$_Person_$_Life __attribute__ ((used, section ("__DATA,__objc_const"))) = {
1,
&_OBJC_PROTOCOL_LifeProtocol
};
// 属性列表
static struct /*_prop_list_t*/ {
unsigned int entsize; // sizeof(struct _prop_t)
unsigned int count_of_properties;
struct _prop_t prop_list[1];
} _OBJC_$_PROP_LIST_Person_$_Life __attribute__ ((used, section ("__DATA,__objc_const"))) = {
sizeof(_prop_t),
1,
{{"name","T@\"NSString\",C,N"}}
};
在翻译后的 C++ 源代码中,我们可以发现一个名称和 Category 相关的结构体定义:_category_t,该结构体表示了 Obj-C 中 Category 的实际结构;_OBJC_$_CATEGORY_Person_$_Life 则就是我们定义的 Person+Life Category。_category_t 结构体中存储了类名、类指针、对象方法列表指针、类方法列表指针、协议列表指针、以及属性列表指针,所以 Category 中支持遵守协议、声明属性、以及定义实现对象方法和类方法(不支持定义成员变量)。当然,在 Apple 开源的 objc4 中,也可以找到 category_t 结构体:
// objc-runtime-new.h
struct category_t {
const char *name;
classref_t cls;
struct method_list_t *instanceMethods;
struct method_list_t *classMethods;
struct protocol_list_t *protocols;
struct property_list_t *instanceProperties;
// Fields below this point are not always present on disk.
// 以下内容并不能保证会在磁盘中展示
struct property_list_t *_classProperties;
method_list_t *methodsForMeta(bool isMeta) {
if (isMeta) return classMethods;
else return instanceMethods;
}
property_list_t *propertiesForMeta(bool isMeta, struct header_info *hi);
};
实现原理
当我们的代码编译完,Category 中的信息就将被存储在 category_t 的结构体中,那么运行时的 Category 又会变成什么样呢?
What
我们尝试分别在 Person 主类、Person+Life 和 Person+Work Category 中定义并实现完全相同的 smile 方法。有个细节是,我们在 Category 中实现主类中已经实现的方法时,编译器会警告「Category is implementing a method which will also be implemented by its primary class」,这又是为什么呢?
// Person.h
@interface Person : NSObject
- (void)smile;
@end
// Person+Life.h
@interface Person (Life) <LifeProtocol>
// ...
- (void)smile;
@end
// Person+Work.h
@interface Person (Work)
- (void)smile;
@end
// main.m
Person *p = [[Person alloc] init];
[p smile];
// OUTPUT:
// Person (Work) - -[Person(Work) smile]
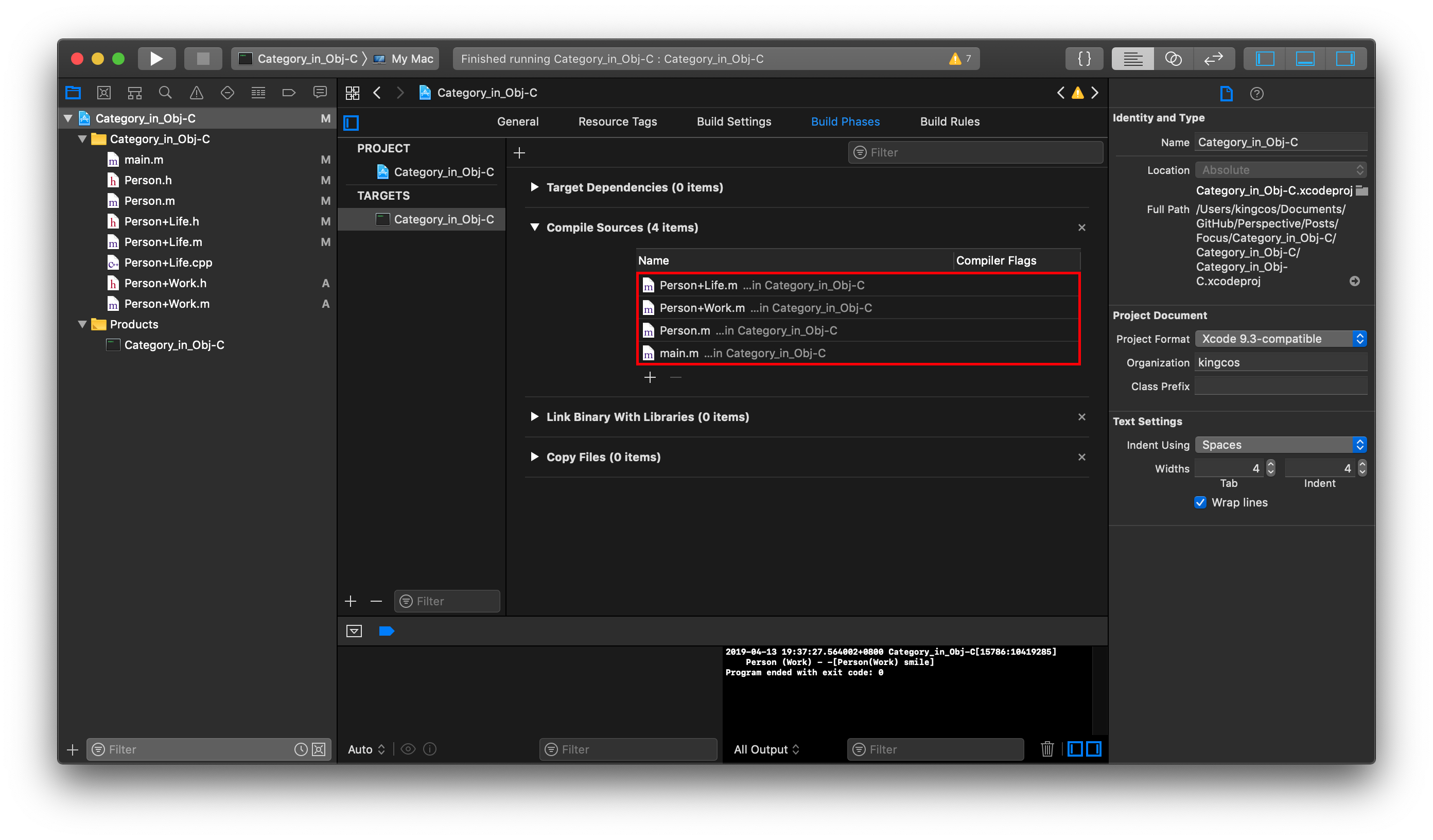
当我们运行程序,发现最终只输出了一句,并且是调用到了 Person+Work Category 中的方法。那么先说结论:当 Category 中实现了主类中同一个方法时,将总是调用 Category 中的方法(这也是为何编译器警告的原因);当存在多个 Category 实现同一个方法时,将总是调用最后被编译的 Category 中的方法。如何查看文件的编译顺序呢?在 Xcode -「Build Phases」-「Compile Sources」中,靠前的即是最先被编译的:
Why
为了证明上述结论,我们需要在 objc4 的源码中,从 Obj-C 运行时初始化的入口着手,即 _objc_init:
// objc-os.mm
/***********************************************************************
* _objc_init
* Bootstrap initialization. Registers our image notifier with dyld.
* 引导初始化。使用 dyld 注册镜像通知器。
* Called by libSystem BEFORE library initialization time
* 在库初始化时间之前由 libSystem 调用
**********************************************************************/
void _objc_init(void)
{
static bool initialized = false;
if (initialized) return;
initialized = true;
// fixme defer initialization until an objc-using image is found?
environ_init();
tls_init();
static_init();
lock_init();
exception_init();
// ➡️ dyld 注册通知;map_images:映射镜像,load_images:加载镜像,unmap_image:反映射镜像
_dyld_objc_notify_register(&map_images, load_images, unmap_image);
}
// objc-runtime-new.mm
/***********************************************************************
* map_images
* Process the given images which are being mapped in by dyld.
* 由 dyld 处理给定将要映射的镜像。
* Calls ABI-agnostic code after taking ABI-specific locks.
* 加上指定 ABI 锁后调用 ABI 无关(agnostic)的代码。
*
* Locking: write-locks runtimeLock
* 锁:写锁 runtimeLock
**********************************************************************/
void
map_images(unsigned count, const char * const paths[],
const struct mach_header * const mhdrs[])
{
// 互斥锁
mutex_locker_t lock(runtimeLock);
// ➡️ map_images_nolock:映射镜像(无锁)
return map_images_nolock(count, paths, mhdrs);
}
// objc-os.mm
void
map_images_nolock(unsigned mhCount, const char * const mhPaths[],
const struct mach_header * const mhdrs[])
{
static bool firstTime = YES;
header_info *hList[mhCount];
uint32_t hCount;
size_t selrefCount = 0;
// Perform first-time initialization if necessary.
// 必要时执行首次初始化。
// This function is called before ordinary library initializers.
// 在普通库构造方法之前调用该函数。
// fixme defer initialization until an objc-using image is found?
if (firstTime) {
preopt_init();
}
// Xcode 中 OBJC_PRINT_IMAGES 环境变量值为 YES 时,将可在控制台打印该信息
// OPTION(PrintImages, OBJC_PRINT_IMAGES, "log image and library names as they are loaded")
if (PrintImages) {
_objc_inform("IMAGES: processing %u newly-mapped images...\n", mhCount);
}
// Find all images with Objective-C metadata.
// 使用 Obj-C 元数据查找所有镜像。
hCount = 0;
// Count classes. Size various table based on the total.
// 计算类。根据总数计算不同的表。
int totalClasses = 0;
int unoptimizedTotalClasses = 0;
{
uint32_t i = mhCount;
// 遍历 mach-o header
while (i--) {
const headerType *mhdr = (const headerType *)mhdrs[i];
// ➡️ addHeader:添加头部信息(计算类的总数、未优化的类总数)
auto hi = addHeader(mhdr, mhPaths[i], totalClasses, unoptimizedTotalClasses);
if (!hi) {
// no objc data in this entry
// 若 hi 为空,则该条目没有 Obj-C 数据
continue;
}
// 判断文件类型是否是可执行文件
// #define MH_EXECUTE 0x2 /* demand paged executable file */
if (mhdr->filetype == MH_EXECUTE) {
// Size some data structures based on main executable's size
// 根据主可执行文件的大小调整一些数据结构的大小
#if __OBJC2__
size_t count;
// 在 __objc_selrefs 节获取 SEL 引用(此处可参考 Mach-O 或 Link Map 文件中 Sections 部分)
// GETSECT(_getObjc2SelectorRefs, SEL, "__objc_selrefs");
_getObjc2SelectorRefs(hi, &count);
selrefCount += count;
// 在 __objc_msgrefs 节获取消息引用
// GETSECT(_getObjc2MessageRefs, message_ref_t, "__objc_msgrefs");
_getObjc2MessageRefs(hi, &count);
selrefCount += count;
#else
_getObjcSelectorRefs(hi, &selrefCount);
#endif
#if SUPPORT_GC_COMPAT
// Halt if this is a GC app.
if (shouldRejectGCApp(hi)) {
_objc_fatal_with_reason
(OBJC_EXIT_REASON_GC_NOT_SUPPORTED,
OS_REASON_FLAG_CONSISTENT_FAILURE,
"Objective-C garbage collection "
"is no longer supported.");
}
#endif
}
// hList 保存 hi 并 hCount 自增
hList[hCount++] = hi;
if (PrintImages) {
_objc_inform("IMAGES: loading image for %s%s%s%s%s\n",
hi->fname(),
mhdr->filetype == MH_BUNDLE ? " (bundle)" : "",
hi->info()->isReplacement() ? " (replacement)" : "",
hi->info()->hasCategoryClassProperties() ? " (has class properties)" : "",
hi->info()->optimizedByDyld()?" (preoptimized)":"");
}
}
}
// Perform one-time runtime initialization that must be deferred until
// the executable itself is found. This needs to be done before
// further initialization.
// (The executable may not be present in this infoList if the
// executable does not contain Objective-C code but Objective-C
// is dynamically loaded later.
// 在找到可执行文件本身之前必须延迟执行一次性运行时初始化。
// 这需要在进一步初始化之前完成。
// (如果可执行文件不包含 Obj-C 代码但 Obj-C 在之后动态加载,则 infoList 中可能不包含该可执行文件。)
if (firstTime) {
sel_init(selrefCount);
arr_init();
#if SUPPORT_GC_COMPAT
// Reject any GC images linked to the main executable.
// We already rejected the app itself above.
// Images loaded after launch will be rejected by dyld.
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < hCount; i++) {
auto hi = hList[i];
auto mh = hi->mhdr();
if (mh->filetype != MH_EXECUTE && shouldRejectGCImage(mh)) {
_objc_fatal_with_reason
(OBJC_EXIT_REASON_GC_NOT_SUPPORTED,
OS_REASON_FLAG_CONSISTENT_FAILURE,
"%s requires Objective-C garbage collection "
"which is no longer supported.", hi->fname());
}
}
#endif
#if TARGET_OS_OSX
// Disable +initialize fork safety if the app is too old (< 10.13).
// Disable +initialize fork safety if the app has a
// __DATA,__objc_fork_ok section.
if (dyld_get_program_sdk_version() < DYLD_MACOSX_VERSION_10_13) {
DisableInitializeForkSafety = true;
if (PrintInitializing) {
_objc_inform("INITIALIZE: disabling +initialize fork "
"safety enforcement because the app is "
"too old (SDK version " SDK_FORMAT ")",
FORMAT_SDK(dyld_get_program_sdk_version()));
}
}
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < hCount; i++) {
auto hi = hList[i];
auto mh = hi->mhdr();
if (mh->filetype != MH_EXECUTE) continue;
unsigned long size;
if (getsectiondata(hi->mhdr(), "__DATA", "__objc_fork_ok", &size)) {
DisableInitializeForkSafety = true;
if (PrintInitializing) {
_objc_inform("INITIALIZE: disabling +initialize fork "
"safety enforcement because the app has "
"a __DATA,__objc_fork_ok section");
}
}
break; // assume only one MH_EXECUTE image
}
#endif
}
if (hCount > 0) {
// ➡️ 读取镜像(传入 header_info 列表,数量,类的总数,未优化的类的总数)
_read_images(hList, hCount, totalClasses, unoptimizedTotalClasses);
}
// 第一次执行完毕后,置为 NO
firstTime = NO;
}
// objc-os.mm
static header_info * addHeader(const headerType *mhdr, const char *path, int &totalClasses, int &unoptimizedTotalClasses)
{
header_info *hi;
if (bad_magic(mhdr)) return NULL;
bool inSharedCache = false;
// Look for hinfo from the dyld shared cache.
// 在 dyld 共享缓存中寻找 hinfo(关于 dyld 共享缓存可参考文末「谈谈 iOS 中的 dyld_shared_cache」一文)。
// 为头部预优化 hinfo
hi = preoptimizedHinfoForHeader(mhdr);
if (hi) {
// Found an hinfo in the dyld shared cache.
// 在 dyld 共享缓存中找到 hinfo
// Weed out duplicates.
// 去除重复(若该 hi 已被加载,则返回空)。
if (hi->isLoaded()) {
return NULL;
}
inSharedCache = true;
// Initialize fields not set by the shared cache
// 初始化未由共享缓存设置的域
// hi->next is set by appendHeader
// hi->next 由 appendHeader 设置
// 设置已加载为 true
hi->setLoaded(true);
// Xcode 中 OBJC_PRINT_PREOPTIMIZATION 环境变量值为 YES 时,将可在控制台打印该信息
// OPTION(PrintPreopt, OBJC_PRINT_PREOPTIMIZATION, "log preoptimization courtesy of dyld shared cache")
if (PrintPreopt) {
_objc_inform("PREOPTIMIZATION: honoring preoptimized header info at %p for %s", hi, hi->fname());
}
#if !__OBJC2__
_objc_fatal("shouldn't be here");
#endif
#if DEBUG
// Verify image_info
// DEBUG 模式校验 image_info
size_t info_size = 0;
const objc_image_info *image_info = _getObjcImageInfo(mhdr,&info_size);
assert(image_info == hi->info());
#endif
}
else
{
// Didn't find an hinfo in the dyld shared cache.
// 在 dyld 共享缓存中未找到 hinfo。
// Weed out duplicates
// 去除重复
for (hi = FirstHeader; hi; hi = hi->getNext()) {
if (mhdr == hi->mhdr()) return NULL;
}
// Locate the __OBJC segment
// 定位 __OBJC 段(Segment)
size_t info_size = 0;
unsigned long seg_size;
// _getObjcImageInfo:内部实际是获取 __objc_imageinfo 数据(__DATA 或 __DATA_CONST 或 __DATA_DIRTY)节(Section)信息
const objc_image_info *image_info = _getObjcImageInfo(mhdr,&info_size);
// getsegmentdata:获取 __OBJC 段数据
// #define SEG_OBJC "__OBJC" /* objective-C runtime segment */
const uint8_t *objc_segment = getsegmentdata(mhdr,SEG_OBJC,&seg_size);
// 若都没有获取到,返回空
if (!objc_segment && !image_info) return NULL;
// Allocate a header_info entry.
// 分配一个 header_info。
// Note we also allocate space for a single header_info_rw in the
// rw_data[] inside header_info.
// 注意我们在 header_info 内部的 rw_data[] 也为单个 header_info_rw 分配了空间。
hi = (header_info *)calloc(sizeof(header_info) + sizeof(header_info_rw), 1);
// Set up the new header_info entry.
// 设置新的 header_info。
hi->setmhdr(mhdr);
#if !__OBJC2__
// mhdr must already be set
hi->mod_count = 0;
hi->mod_ptr = _getObjcModules(hi, &hi->mod_count);
#endif
// Install a placeholder image_info if absent to simplify code elsewhere
// 如果没有在其他地方简化代码则安装占位符 image_info
static const objc_image_info emptyInfo = {0, 0};
hi->setinfo(image_info ?: &emptyInfo);
// 设置已加载为 true
hi->setLoaded(true);
hi->setAllClassesRealized(NO);
}
#if __OBJC2__
{
size_t count = 0;
// 在 __objc_classlist 节获取类列表
// GETSECT(_getObjc2ClassList, classref_t, "__objc_classlist");
if (_getObjc2ClassList(hi, &count)) {
// totalClasses 设置为获取到的类数量
totalClasses += (int)count;
// 若获取的 header_info 不在共享缓存中,则视为未优化类,更新 unoptimizedTotalClasses
if (!inSharedCache) unoptimizedTotalClasses += count;
}
}
#endif
appendHeader(hi);
return hi;
}
// objc-runtime-new.mm
/***********************************************************************
* _read_images
* Perform initial processing of the headers in the linked
* list beginning with headerList.
* 从 headerList 开始为链表中的头部执行初始处理。
*
* Called by: map_images_nolock
* 由 map_images_nolock 调用
*
* Locking: runtimeLock acquired by map_images
* 锁:由 map_images 获得的 runtimeLock
**********************************************************************/
void _read_images(header_info **hList, uint32_t hCount, int totalClasses, int unoptimizedTotalClasses)
{
header_info *hi;
uint32_t hIndex;
size_t count;
size_t i;
Class *resolvedFutureClasses = nil;
size_t resolvedFutureClassCount = 0;
static bool doneOnce;
TimeLogger ts(PrintImageTimes);
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
#define EACH_HEADER \
hIndex = 0; \
hIndex < hCount && (hi = hList[hIndex]); \
hIndex++
if (!doneOnce) {
doneOnce = YES;
#if SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISA
// Disable non-pointer isa under some conditions.
# if SUPPORT_INDEXED_ISA
// Disable nonpointer isa if any image contains old Swift code
for (EACH_HEADER) {
if (hi->info()->containsSwift() &&
hi->info()->swiftVersion() < objc_image_info::SwiftVersion3)
{
DisableNonpointerIsa = true;
if (PrintRawIsa) {
_objc_inform("RAW ISA: disabling non-pointer isa because "
"the app or a framework contains Swift code "
"older than Swift 3.0");
}
break;
}
}
# endif
# if TARGET_OS_OSX
// Disable non-pointer isa if the app is too old
// (linked before OS X 10.11)
if (dyld_get_program_sdk_version() < DYLD_MACOSX_VERSION_10_11) {
DisableNonpointerIsa = true;
if (PrintRawIsa) {
_objc_inform("RAW ISA: disabling non-pointer isa because "
"the app is too old (SDK version " SDK_FORMAT ")",
FORMAT_SDK(dyld_get_program_sdk_version()));
}
}
// Disable non-pointer isa if the app has a __DATA,__objc_rawisa section
// New apps that load old extensions may need this.
for (EACH_HEADER) {
if (hi->mhdr()->filetype != MH_EXECUTE) continue;
unsigned long size;
if (getsectiondata(hi->mhdr(), "__DATA", "__objc_rawisa", &size)) {
DisableNonpointerIsa = true;
if (PrintRawIsa) {
_objc_inform("RAW ISA: disabling non-pointer isa because "
"the app has a __DATA,__objc_rawisa section");
}
}
break; // assume only one MH_EXECUTE image
}
# endif
#endif
if (DisableTaggedPointers) {
disableTaggedPointers();
}
initializeTaggedPointerObfuscator();
if (PrintConnecting) {
_objc_inform("CLASS: found %d classes during launch", totalClasses);
}
// namedClasses
// Preoptimized classes don't go in this table.
// 4/3 is NXMapTable's load factor
int namedClassesSize =
(isPreoptimized() ? unoptimizedTotalClasses : totalClasses) * 4 / 3;
gdb_objc_realized_classes =
NXCreateMapTable(NXStrValueMapPrototype, namedClassesSize);
allocatedClasses = NXCreateHashTable(NXPtrPrototype, 0, nil);
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: first time tasks");
}
// Discover classes. Fix up unresolved future classes. Mark bundle classes.
for (EACH_HEADER) {
classref_t *classlist = _getObjc2ClassList(hi, &count);
if (! mustReadClasses(hi)) {
// Image is sufficiently optimized that we need not call readClass()
continue;
}
bool headerIsBundle = hi->isBundle();
bool headerIsPreoptimized = hi->isPreoptimized();
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Class cls = (Class)classlist[i];
Class newCls = readClass(cls, headerIsBundle, headerIsPreoptimized);
if (newCls != cls && newCls) {
// Class was moved but not deleted. Currently this occurs
// only when the new class resolved a future class.
// Non-lazily realize the class below.
resolvedFutureClasses = (Class *)
realloc(resolvedFutureClasses,
(resolvedFutureClassCount+1) * sizeof(Class));
resolvedFutureClasses[resolvedFutureClassCount++] = newCls;
}
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: discover classes");
// Fix up remapped classes
// Class list and nonlazy class list remain unremapped.
// Class refs and super refs are remapped for message dispatching.
if (!noClassesRemapped()) {
for (EACH_HEADER) {
Class *classrefs = _getObjc2ClassRefs(hi, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
remapClassRef(&classrefs[i]);
}
// fixme why doesn't test future1 catch the absence of this?
classrefs = _getObjc2SuperRefs(hi, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
remapClassRef(&classrefs[i]);
}
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: remap classes");
// Fix up @selector references
static size_t UnfixedSelectors;
{
mutex_locker_t lock(selLock);
for (EACH_HEADER) {
if (hi->isPreoptimized()) continue;
bool isBundle = hi->isBundle();
SEL *sels = _getObjc2SelectorRefs(hi, &count);
UnfixedSelectors += count;
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
const char *name = sel_cname(sels[i]);
sels[i] = sel_registerNameNoLock(name, isBundle);
}
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: fix up selector references");
#if SUPPORT_FIXUP
// Fix up old objc_msgSend_fixup call sites
for (EACH_HEADER) {
message_ref_t *refs = _getObjc2MessageRefs(hi, &count);
if (count == 0) continue;
if (PrintVtables) {
_objc_inform("VTABLES: repairing %zu unsupported vtable dispatch "
"call sites in %s", count, hi->fname());
}
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
fixupMessageRef(refs+i);
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: fix up objc_msgSend_fixup");
#endif
// Discover protocols. Fix up protocol refs.
for (EACH_HEADER) {
extern objc_class OBJC_CLASS_$_Protocol;
Class cls = (Class)&OBJC_CLASS_$_Protocol;
assert(cls);
NXMapTable *protocol_map = protocols();
bool isPreoptimized = hi->isPreoptimized();
bool isBundle = hi->isBundle();
protocol_t **protolist = _getObjc2ProtocolList(hi, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
readProtocol(protolist[i], cls, protocol_map,
isPreoptimized, isBundle);
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: discover protocols");
// Fix up @protocol references
// Preoptimized images may have the right
// answer already but we don't know for sure.
for (EACH_HEADER) {
protocol_t **protolist = _getObjc2ProtocolRefs(hi, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
remapProtocolRef(&protolist[i]);
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: fix up @protocol references");
// Realize non-lazy classes (for +load methods and static instances)
for (EACH_HEADER) {
classref_t *classlist =
_getObjc2NonlazyClassList(hi, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Class cls = remapClass(classlist[i]);
if (!cls) continue;
// hack for class __ARCLite__, which didn't get this above
#if TARGET_OS_SIMULATOR
if (cls->cache._buckets == (void*)&_objc_empty_cache &&
(cls->cache._mask || cls->cache._occupied))
{
cls->cache._mask = 0;
cls->cache._occupied = 0;
}
if (cls->ISA()->cache._buckets == (void*)&_objc_empty_cache &&
(cls->ISA()->cache._mask || cls->ISA()->cache._occupied))
{
cls->ISA()->cache._mask = 0;
cls->ISA()->cache._occupied = 0;
}
#endif
addClassTableEntry(cls);
realizeClass(cls);
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: realize non-lazy classes");
// Realize newly-resolved future classes, in case CF manipulates them
if (resolvedFutureClasses) {
for (i = 0; i < resolvedFutureClassCount; i++) {
realizeClass(resolvedFutureClasses[i]);
resolvedFutureClasses[i]->setInstancesRequireRawIsa(false/*inherited*/);
}
free(resolvedFutureClasses);
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: realize future classes");
// ➡️ Category
// Discover categories.
// 发现 Category。
// 遍历 hList 中的 header_info
for (EACH_HEADER) {
// 在 __objc_catlist 节获取 Category 列表
// GETSECT(_getObjc2CategoryList, category_t *, "__objc_catlist");
category_t **catlist =
_getObjc2CategoryList(hi, &count);
bool hasClassProperties = hi->info()->hasCategoryClassProperties();
// 遍历 Category
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
// 获取第 i 个 Category,类型为 category_t
category_t *cat = catlist[i];
// 根据 Category 的 cls 重新映射类
Class cls = remapClass(cat->cls);
// 类为空时
if (!cls) {
// Category's target class is missing (probably weak-linked).
// Category 的目标类丢失(可能为弱链接)。
// Disavow any knowledge of this category.
// 否认对此 Category 的任何了解。
// 将 Category 置为 nil
catlist[i] = nil;
if (PrintConnecting) {
_objc_inform("CLASS: IGNORING category \?\?\?(%s) %p with "
"missing weak-linked target class",
cat->name, cat);
}
continue;
}
// 类非空时
// Process this category.
// First, register the category with its target class.
// Then, rebuild the class's method lists (etc) if
// the class is realized.
// 处理该 Category。
// 首先,使用目标类注册 Category。
// 然后,如果实现了类,则重建类的方法列表(等)。
bool classExists = NO;
// 判断 Category 中存在对象方法、协议、或属性
if (cat->instanceMethods || cat->protocols
|| cat->instanceProperties)
{
// 记录未附加上的 Category
addUnattachedCategoryForClass(cat, cls, hi);
if (cls->isRealized()) {
// ➡️ 如果实现了类,重建类
remethodizeClass(cls);
classExists = YES;
}
if (PrintConnecting) {
_objc_inform("CLASS: found category -%s(%s) %s",
cls->nameForLogging(), cat->name,
classExists ? "on existing class" : "");
}
}
// 判断 Category 中存在类方法、协议、或类属性
if (cat->classMethods || cat->protocols
|| (hasClassProperties && cat->_classProperties))
{
// 记录未附加上的 Category
addUnattachedCategoryForClass(cat, cls->ISA(), hi);
if (cls->ISA()->isRealized()) {
// ➡️ 如果实现了元类,重建元类
remethodizeClass(cls->ISA());
}
if (PrintConnecting) {
_objc_inform("CLASS: found category +%s(%s)",
cls->nameForLogging(), cat->name);
}
}
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: discover categories");
// Category discovery MUST BE LAST to avoid potential races
// when other threads call the new category code before
// this thread finishes its fixups.
// +load handled by prepare_load_methods()
if (DebugNonFragileIvars) {
realizeAllClasses();
}
// Print preoptimization statistics
if (PrintPreopt) {
static unsigned int PreoptTotalMethodLists;
static unsigned int PreoptOptimizedMethodLists;
static unsigned int PreoptTotalClasses;
static unsigned int PreoptOptimizedClasses;
for (EACH_HEADER) {
if (hi->isPreoptimized()) {
_objc_inform("PREOPTIMIZATION: honoring preoptimized selectors "
"in %s", hi->fname());
}
else if (hi->info()->optimizedByDyld()) {
_objc_inform("PREOPTIMIZATION: IGNORING preoptimized selectors "
"in %s", hi->fname());
}
classref_t *classlist = _getObjc2ClassList(hi, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Class cls = remapClass(classlist[i]);
if (!cls) continue;
PreoptTotalClasses++;
if (hi->isPreoptimized()) {
PreoptOptimizedClasses++;
}
const method_list_t *mlist;
if ((mlist = ((class_ro_t *)cls->data())->baseMethods())) {
PreoptTotalMethodLists++;
if (mlist->isFixedUp()) {
PreoptOptimizedMethodLists++;
}
}
if ((mlist=((class_ro_t *)cls->ISA()->data())->baseMethods())) {
PreoptTotalMethodLists++;
if (mlist->isFixedUp()) {
PreoptOptimizedMethodLists++;
}
}
}
}
_objc_inform("PREOPTIMIZATION: %zu selector references not "
"pre-optimized", UnfixedSelectors);
_objc_inform("PREOPTIMIZATION: %u/%u (%.3g%%) method lists pre-sorted",
PreoptOptimizedMethodLists, PreoptTotalMethodLists,
PreoptTotalMethodLists
? 100.0*PreoptOptimizedMethodLists/PreoptTotalMethodLists
: 0.0);
_objc_inform("PREOPTIMIZATION: %u/%u (%.3g%%) classes pre-registered",
PreoptOptimizedClasses, PreoptTotalClasses,
PreoptTotalClasses
? 100.0*PreoptOptimizedClasses/PreoptTotalClasses
: 0.0);
_objc_inform("PREOPTIMIZATION: %zu protocol references not "
"pre-optimized", UnfixedProtocolReferences);
}
#undef EACH_HEADER
}
// objc-runtime-new.mm
/***********************************************************************
* remethodizeClass
* Attach outstanding categories to an existing class.
* 将未完成的 Category 附加到现有类。
* Fixes up cls's method list, protocol list, and property list.
* 修复 cls 的方法列表、协议列表、以及属性列表。
* Updates method caches for cls and its subclasses.
* 更新 cls 以及其子类的方法缓存。
* Locking: runtimeLock must be held by the caller
* 锁:调用者必须持有 runtimeLock
**********************************************************************/
static void remethodizeClass(Class cls)
{
// Category 列表
category_list *cats;
bool isMeta;
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
// 是否为元类
isMeta = cls->isMetaClass();
// Re-methodizing: check for more categories
// 重新方法化:检查更多的 Category
if ((cats = unattachedCategoriesForClass(cls, false/*not realizing*/))) {
if (PrintConnecting) {
_objc_inform("CLASS: attaching categories to class '%s' %s",
cls->nameForLogging(), isMeta ? "(meta)" : "");
}
// ➡️ 附加 Category(类/元类,Category,是否刷新缓存)
attachCategories(cls, cats, true /*flush caches*/);
free(cats);
}
}
// objc-runtime-new.mm
// Attach method lists and properties and protocols from categories to a class.
// 将所有 Category 的方法列表、属性列表、协议列表附加到类上。
// Assumes the categories in cats are all loaded and sorted by load order,
// oldest categories first.
// 假设 cats 中的 Category 都已加载并由加载顺序排序,则最后(编译)的 Category 排在最先。
static void
attachCategories(Class cls, category_list *cats, bool flush_caches)
{
if (!cats) return;
// ➡️ Xcode 中 OBJC_PRINT_REPLACED_METHODS 环境变量值为 YES 时,将可在控制台打印该信息
// OPTION(PrintReplacedMethods, OBJC_PRINT_REPLACED_METHODS, "log methods replaced by category implementations")
if (PrintReplacedMethods) printReplacements(cls, cats);
// 是否是元类
bool isMeta = cls->isMetaClass();
// fixme rearrange to remove these intermediate allocations
// 方法列表(指向指针的指针,存储了两维:eg. [[cat_1->method_a, cat_1->method_b], [cat_2->method_c, cat_2->method_d]])
method_list_t **mlists = (method_list_t **)
malloc(cats->count * sizeof(*mlists));
// 属性列表
property_list_t **proplists = (property_list_t **)
malloc(cats->count * sizeof(*proplists));
// 协议列表
protocol_list_t **protolists = (protocol_list_t **)
malloc(cats->count * sizeof(*protolists));
// Count backwards through cats to get newest categories first
int mcount = 0;
int propcount = 0;
int protocount = 0;
// i = Category 的个数
int i = cats->count;
bool fromBundle = NO;
// ➡️ 将所有 Category 中的方法、属性、协议提取出
// 倒数 i
while (i--) {
// entry = 一个 Category
auto& entry = cats->list[i];
// mlist = Category 中的方法列表
method_list_t *mlist = entry.cat->methodsForMeta(isMeta);
if (mlist) {
mlists[mcount++] = mlist;
fromBundle |= entry.hi->isBundle();
}
// proplist = Category 中的属性列表
property_list_t *proplist =
entry.cat->propertiesForMeta(isMeta, entry.hi);
if (proplist) {
proplists[propcount++] = proplist;
}
// protolist = Category 中的协议列表
protocol_list_t *protolist = entry.cat->protocols;
if (protolist) {
protolists[protocount++] = protolist;
}
}
// rw = 类/元类对象的 class_rw_t *data()
auto rw = cls->data();
prepareMethodLists(cls, mlists, mcount, NO, fromBundle);
// ➡️ Category 方法列表 -> 类/元类方法列表,方法列表数量(上述二维中第一维的大小)
rw->methods.attachLists(mlists, mcount);
free(mlists);
if (flush_caches && mcount > 0) flushCaches(cls);
// ➡️ Category 属性列表 -> 类/元类属性列表,属性列表数量(上述二维中第一维的大小)
rw->properties.attachLists(proplists, propcount);
free(proplists);
// ➡️ Category 协议列表 -> 类/元类协议列表,协议列表数量(上述二维中第一维的大小)
rw->protocols.attachLists(protolists, protocount);
free(protolists);
}
// objc-runtime-new.h
class list_array_tt {
public:
void attachLists(List* const * addedLists, uint32_t addedCount) {
if (addedCount == 0) return;
if (hasArray()) {
// many lists -> many lists
// oldCount = 原有的大小
uint32_t oldCount = array()->count;
// newCount = 原有 + 新增
uint32_t newCount = oldCount + addedCount;
// realloc 重新分配内存空间(扩容)
setArray((array_t *)realloc(array(), array_t::byteSize(newCount)));
// 设置为新大小
array()->count = newCount;
// array()->lists 为原有列表的指针
// 将指针指向的内存内容向后偏移 addedCount
// void *memmove(void *__dst, const void *__src, size_t __len);
memmove(array()->lists + addedCount, array()->lists,
oldCount * sizeof(array()->lists[0]));
// addedLists 为所有 Category 中相应列表(如方法列表等)的指针
// 将指针指向的内存内容拷贝到原有列表的指针地址处
// void *memcpy(void *__dst, const void *__src, size_t __n);
memcpy(array()->lists, addedLists,
addedCount * sizeof(array()->lists[0]));
}
else if (!list && addedCount == 1) {
// 0 lists -> 1 list
list = addedLists[0];
}
else {
// 1 list -> many lists
List* oldList = list;
uint32_t oldCount = oldList ? 1 : 0;
uint32_t newCount = oldCount + addedCount;
setArray((array_t *)malloc(array_t::byteSize(newCount)));
array()->count = newCount;
if (oldList) array()->lists[addedCount] = oldList;
memcpy(array()->lists, addedLists,
addedCount * sizeof(array()->lists[0]));
}
}
};
从 realloc 到 memmove 和 memcpy 部分可以参考下图:
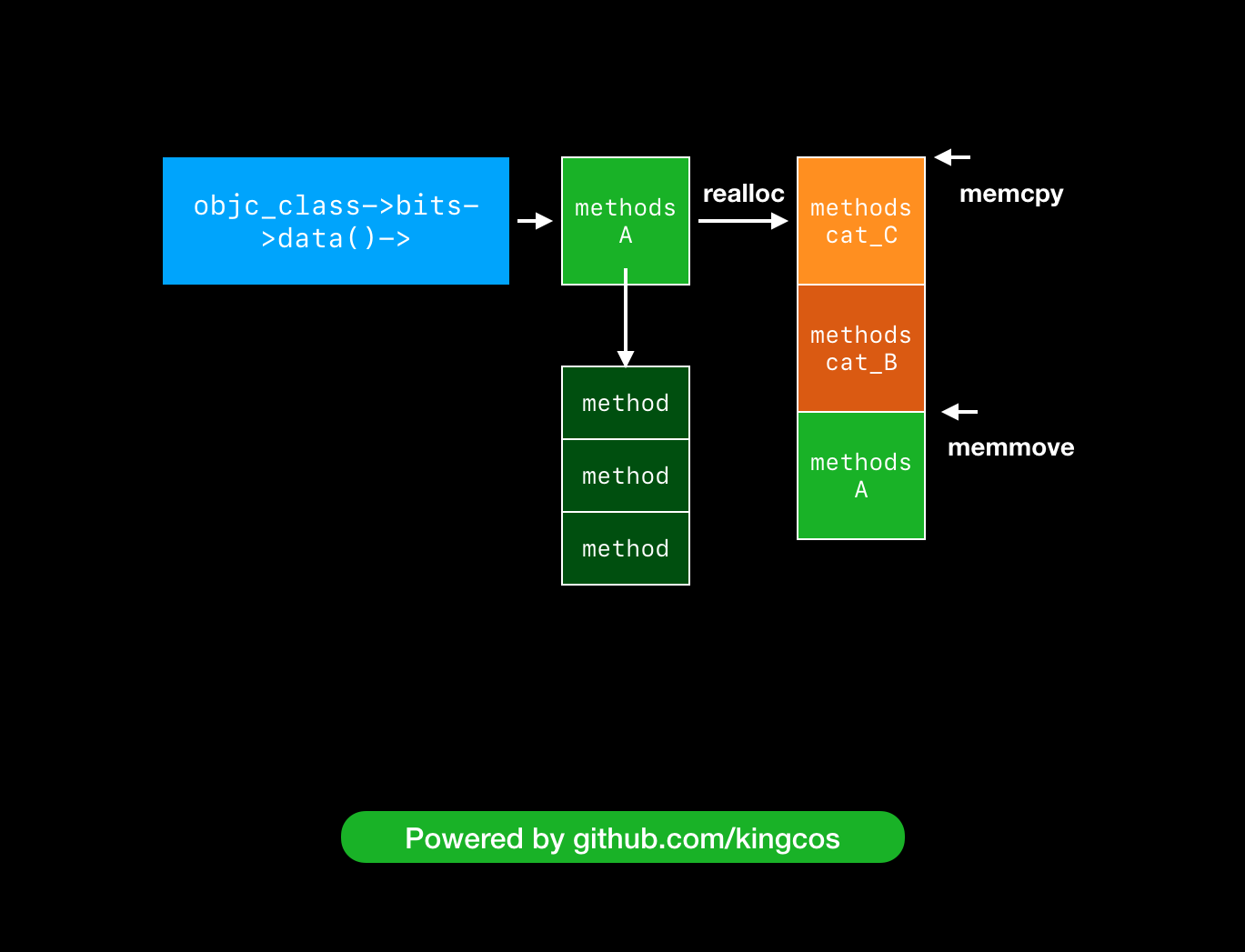
因此,对于 Category 在运行时将其中的方法、属性、协议加载到主类的过程搞明白后,之前的结论就水落石出。越靠后编译的 Category,其方法列表最终就越靠前。因此在调用时,虽然主类和其他 Category 中的方法并没有被覆盖,但会因为在前面已经被找到并调用而无法调用到。也是因为方法并没有被覆盖,如果我们在 Category 中仅声明却不实现,运行时仍将找到主类中的实现。从上面源码分析中我们也可以发现,在 Xcode 设置 OBJC_PRINT_REPLACED_METHODS 环境变量为 YES 后,就可以在运行时输出所有被替换的方法(若添加后仍未输出我们自定义类的替换信息,可以在尝试主类和所有 Category 中添加 + (void)load 方法实现后重试):
objc[17895]: REPLACED: -[Person smile] by category Life (IMP was 0x100001b90 (/Users/kingcos/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/Category_in_Obj-C-cgesibqaizbvgnckrzeofmpfkmmy/Build/Products/Debug/Category_in_Obj-C), now 0x100001b00 (/Users/kingcos/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/Category_in_Obj-C-cgesibqaizbvgnckrzeofmpfkmmy/Build/Products/Debug/Category_in_Obj-C))
objc[17895]: REPLACED: -[Person smile] by category Work (IMP was 0x100001b00 (/Users/kingcos/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/Category_in_Obj-C-cgesibqaizbvgnckrzeofmpfkmmy/Build/Products/Debug/Category_in_Obj-C), now 0x100001b40 (/Users/kingcos/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/Category_in_Obj-C-cgesibqaizbvgnckrzeofmpfkmmy/Build/Products/Debug/Category_in_Obj-C))
第一条的替换,是指 Person+Life 替换了 Person 中的 smile 方法,而第二条指 Person+Work 再次替换了 Person+Life 中的 smile 方法,因此最终也由 Person+Work 中的方法被调用,最终也与我们的结论一致。
memmove & memcpy
上一节中,Category 中内容列表与主类融合时,调用了 memmove 和 memcpy 函数,它们其实是 C 语言标准库中的函数,目的都是将一定长度的源内存地址的内容拷贝到目标内存地址中。在 Apple 开源的 XNU - libsyscall 中,memmove 和 memcpy 本质其实是一致的:
// _libc_funcptr.c
__attribute__((visibility("hidden")))
void *
memmove(void *dst, const void *src, size_t n)
{
return _libkernel_string_functions->memmove(dst, src, n);
}
__attribute__((visibility("hidden")))
void *
memcpy(void *dst, const void *src, size_t n)
{
return _libkernel_string_functions->memmove(dst, src, n);
}
// _libc_funcptr.c
/*
* Upcalls to optimized libplatform string functions
*/
static const struct _libkernel_string_functions
_libkernel_generic_string_functions = {
.bzero = _libkernel_bzero,
.memmove = _libkernel_memmove,
.memset = _libkernel_memset,
.strchr = _libkernel_strchr,
.strcmp = _libkernel_strcmp,
.strcpy = _libkernel_strcpy,
.strlcpy = _libkernel_strlcpy,
.strlen = _libkernel_strlen,
};
static _libkernel_string_functions_t _libkernel_string_functions =
&_libkernel_generic_string_functions;
// memcpy.c
/*
* sizeof(word) MUST BE A POWER OF TWO
* SO THAT wmask BELOW IS ALL ONES
*/
typedef int word; /* "word" used for optimal copy speed "字"用作优化拷贝速度 */
#define wsize sizeof(word)
#define wmask (wsize - 1)
/*
* Copy a block of memory, handling overlap.
* 拷贝一块内存,并处理重叠部分。
* This is the routine that actually implements
* (the portable versions of) bcopy, memcpy, and memmove.
* 这是个实际实现了(可移植版本的)bcopy、memcpy、以及 memmove 的例行程序。
*/
// visibility("hidden"):隐藏函数符号
__attribute__((visibility("hidden")))
void * _libkernel_memmove(void *dst0, const void *src0, size_t length)
{
// 保存一份目标、源,但源是常量,而目标是可变的
char *dst = dst0;
const char *src = src0;
size_t t;
// 长度为 0 或目标等于源时,无需移动
if (length == 0 || dst == src) /* nothing to do */
goto done;
/*
* Macros: loop-t-times; and loop-t-times, t>0
* 定义循环宏,t 大于 0 时,循环 t 次
*/
#define TLOOP(s) if (t) TLOOP1(s)
#define TLOOP1(s) do { s; } while (--t)
// 如果源 > 目标(高地址 -> 低地址,小端就是向前)
printf("(unsigned long)dst: %lu; (unsigned long)src: %lu\n", (unsigned long)dst, (unsigned long)src);
if ((unsigned long)dst < (unsigned long)src) {
/*
* Copy forward.
* 正向拷贝。
*/
// typedef unsigned long uintptr_t;
t = (uintptr_t)src; /* only need low bits 只需要低位 */
printf("(t | (uintptr_t)dst) & wmask: %lu\n", (t | (uintptr_t)dst) & wmask);
if ((t | (uintptr_t)dst) & wmask) {
/*
* Try to align operands. This cannot be done
* unless the low bits match.
* 尝试对齐操作数。除非低位匹配,否则不可这样做。
*/
if ((t ^ (uintptr_t)dst) & wmask || length < wsize)
t = length;
else
t = wsize - (t & wmask);
length -= t;
//
// TLOOP1(*dst++ = *src++);
do {
*dst++ = *src++;
} while (--t);
}
/*
* Copy whole words, then mop up any trailing bytes.
* 拷贝整个字,然后删除所有尾字节。
*/
t = length / wsize;
printf("t: %zu\n", t);
// TLOOP(*(word *)dst = *(word *)src; src += wsize; dst += wsize);
if (t) {
do {
// 更改指针指向的一个字长的内容(src -> dst)
*(word *)dst = *(word *)src;
// dst & src 向前移动一个字长
src += wsize;
dst += wsize;
} while (--t);
}
printf("(unsigned long)dst: %lu; (unsigned long)src: %lu\n", (unsigned long)dst, (unsigned long)src);
t = length & wmask;
printf("t: %zu\n", t);
// TLOOP(*dst++ = *src++);
if (t) {
do {
*dst++ = *src++;
} while (--t);
}
} else {
/*
* Copy backwards. Otherwise essentially the same.
* Alignment works as before, except that it takes
* (t&wmask) bytes to align, not wsize-(t&wmask).
* 反向拷贝。否则基本一致。
* 与之前一样对齐,除了它是以 (t&wmask) 字节对齐,而非 wsize-(t&wmask)。
*/
src += length;
dst += length;
t = (uintptr_t)src;
printf("(t | (uintptr_t)dst) & wmask: %lu\n", (t | (uintptr_t)dst) & wmask);
if ((t | (uintptr_t)dst) & wmask) {
if ((t ^ (uintptr_t)dst) & wmask || length <= wsize)
t = length;
else
t &= wmask;
length -= t;
// TLOOP1(*--dst = *--src);
do {
*--dst = *--src;
} while (--t);
}
t = length / wsize;
// TLOOP(src -= wsize; dst -= wsize; *(word *)dst = *(word *)src);
if (t) {
do {
src -= wsize;
dst -= wsize;
*(word *)dst = *(word *)src;
} while (--t);
}
t = length & wmask;
// TLOOP(*--dst = *--src);
if (t) {
do {
*--dst = *--src;
} while (--t);
}
}
done:
printf("(unsigned long)dst: %lu; (unsigned long)src: %lu\n", (unsigned long)dst, (unsigned long)src);
return (dst0);
}
我已经将该函数移植到 Demo 中,可以尝试低地址拷贝到高地址,也可以将高地址拷贝到低地址:
// b -> a
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
NSLog(@"Before: a: %d, b: %d", a, b);
_libkernel_memmove(&a, &b, sizeof(int));
// memmove(&a, &b, sizeof(int));
// memcpy(&a, &b, sizeof(int));
NSLog(@"After: a: %d, b: %d", a, b);
// OUTPUT:
// Before: a: 10, b: 20
// After: a: 20, b: 20
// c -> d
int c = 30;
int d = 40;
NSLog(@"Before: c: %d, d: %d", c, d);
// _libkernel_memmove2 是个简化版本的 _libkernel_memmove
_libkernel_memmove2(&d, &c, sizeof(int));
NSLog(@"After: c: %d, d: %d", c, d);
// OUTPUT:
// Before: c: 30, d: 40
// After: c: 30, d: 30
但在有些编译器中,由于不同的标准库具体实现可能会有所不同。其中最主要的差别便是 memcpy 的实现通常并非一定是安全的,当源内存和目标内存存在重叠时,memcpy 将发生错误:
#include <stddef.h> /* size_t */
void *c_memcpy(void *dest, const void *src, size_t n)
{
char *dp = dest;
const char *sp = src;
while (n--)
*dp++ = *sp++;
return dest;
}
上面是 C99 标准库中的实现。下面尝试下,将一个数组的前半截拷贝到其中间的地址,这样源地址与目标地址就出现了重叠部分。需要注意的是,开发者要保证内存是已经分配好的,如果目标地址无法容纳足够长的源地址内容长度,则仍将溢出,发生崩溃。
// e[0, 1] -> e[1, 2]
int e[5] = {1, 2, 3};
NSLog(@"Before: e[0]: %d, e[1]: %d, e[2]: %d, e[3]: %d, e[4]: %d", e[0], e[1], e[2], e[3], e[4]);
_libkernel_memmove3(&e[2], &e[0], sizeof(int) * 3);
NSLog(@"After: e[0]: %d, e[1]: %d, e[2]: %d, e[3]: %d, e[4]: %d", e[0], e[1], e[2], e[3], e[4]);
/ OUTPUT:
// Before: e[0]: 1, e[1]: 2, e[2]: 3, e[3]: 0, e[4]: 0
// After: e[0]: 1, e[1]: 2, e[2]: 1, e[3]: 2, e[4]: 3
// f[0, 1] -> f[1, 2]
int f[5] = {1, 2, 3};
NSLog(@"Before: f[0]: %d, f[1]: %d, f[2]: %d, f[3]: %d, f[4]: %d", f[0], f[1], f[2], f[3], f[4]);
v_memcpy(&f[2], &f[0], sizeof(int) * 3);
NSLog(@"After: f[0]: %d, f[1]: %d, f[2]: %d, f[3]: %d, f[4]: %d", f[0], f[1], f[2], f[3], f[4]);
// OUTPUT:
// Before: f[0]: 1, f[1]: 2, f[2]: 3, f[3]: 0, f[4]: 0
// After: f[0]: 1, f[1]: 2, f[2]: 1, f[3]: 2, f[4]: 1
结果很明显,c_memcpy(C99 标准库实现的 memcpy)在重叠部分出现了差错,而 memmove 却能够正确的处理。这是因为在 memmove 内部会判断源地址和目标地址的大小,进而进行正向或反向拷贝,从而避免了丢弃数据。
